DHCP for Beginners
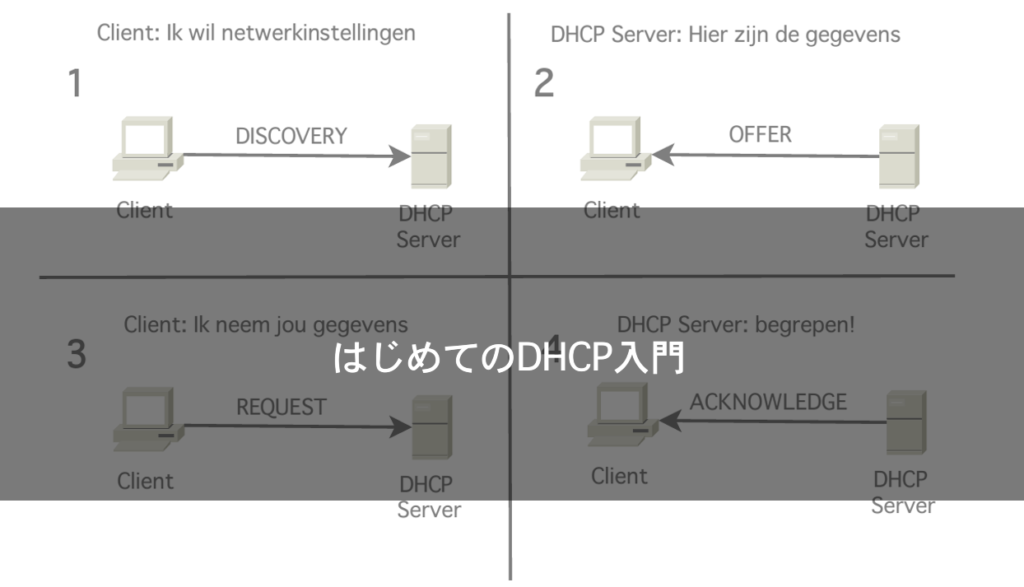
table of contents
My name is Ito and I am an infrastructure engineer
Have you heard of DHCP?
It's actually something that's all around us.
Do you have internet access at home or at work?
If you can do it, then there is a good chance that you are already using DHCP
This article aims to shed some light on DHCP, which operates behind the scenes
What is DHCP?
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, and roughly speaking, a protocol that assigns configuration information to clients within a network so that they can communicate .
When you connect a LAN cable to your PC, the DHCP server will provide you with a pooled IP address, as well as information about the gateway and DNS server, which will then be configured
This means that you can simply plug in the LAN cable and start up the PC, and there is no need to configure the network
In this case, there is a DHCP server within the LAN, and the PC that is assigned an IP address by that server is called DHCP client
Your home PC can probably access the Internet without any "network settings." This is "DHCP." At home, the router usually handles the DHCP function
Here are some of the settings you can configure on your DHCP server:
- IP address
- Subnet mask
- Default Gateway
- DNS Server
There are other DHCP settings like this:
- Lease periods for various addresses
- Scope (subnet range) settings
- Setting up a reservation to assign a fixed IP to a specific PC
Here's a brief explanation of each of the three settings:
| Lease period | The period during which the assigned IP address can be used; when the lease period expires, the DHCP client obtains a new IP address |
| scope | 1 scope = 1 subnet. For example, "192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.129" and "192.168.1.130 to 192.168.1.253" are each a scope |
| reservation | A function that continues to assign the same IP address to a DHCP client (e.g., server) with a specific function |
This is how it is possible to set up, but how does DHCP assign IP addresses?
More specific details about DHCP
To use DHCP, the DHCP client must be able to receive an IP address.
DHCP is a protocol that dynamically configures hosts, so DHCP client C must be in a state where network settings can be dynamically configured.
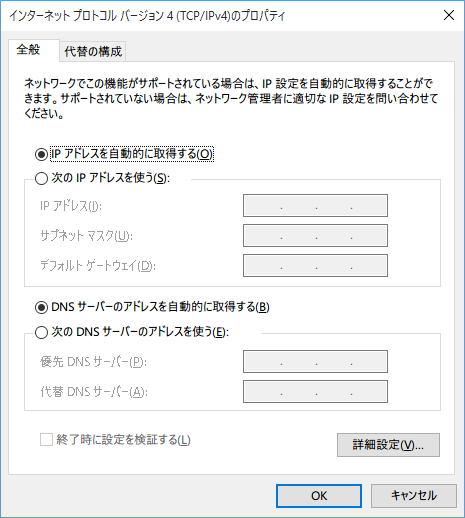
This is what it looks like on Windows. By default, Windows is set to receive DHCP, so you don't need to worry too much about it
In Windows 10, you can check this
by going to [Control Panel] - [Network and Sharing Center] - [Change adapter settings] and checking the properties of the network in question.
If you need to assign a static IP address, assign it manually as described above
When a DHCP client receives an IP address
Here is a brief summary of the process that a DHCP client goes through to receive an IP address
- When the client starts up, it broadcasts a request for an IP address (DHCPDISCOVER)
- The DHCP server broadcasts the IP address (DHCPOFFER)
- The client broadcasts a request saying "I'll use this IP address" (DHHCPREQUEST)
- The DHCP server responds with OK/NG (DHCPACK/DHCPNAK)
What do you think? The key is to exchange messages multiple times via broadcasting, since the IP address has not yet been determined
It is also assumed that there will be multiple DHCP servers
When the IP address lease is about to expire
When an IP address is assigned, the assigned IP address is linked to the MAC address of the DHCP client and the lease period of the IP address is managed. Therefore, even if the DHCP client and server do not communicate, the IP address will remain assigned
However, if the lease period expires and no communication is made, the IP address will be returned to the DHCP server.
When the device is connected to the network, the same process as when it was received will be carried out.
Now, let me explain the process of leasing in more detail
- When the lease period is half over, the server requests an extension of the IP address (performs the same operation as when the IP address is received)
- If an extension request is sent to the DHCP server and there is no response (DHCPACK), the request will fail
- Periodically send renewal requests to the DHCP server
- If the lease expires without a response, the IP address will be terminated
What do you think? The clever thing about DHCP is that it basically tries to use the same IP address.
By doing this, you don't have to think about setting the IP address again.
This means that the load on the DHCP server doesn't increase.
This is how DHCP works.
So why does a protocol called DHCP exist?
You might be thinking, "Why not just assign everything statically?"
What are the benefits of DHCP?
If you don't use DHCP, you'll have to set the IP address/gateway/DNS server for each device...
just thinking about it is scary.
This will be a great benefit for administrators in the company's systems department,
because if you assign IP addresses statically, you have to manage which terminals have which IP addresses.
The great thing about this is that it allows for centralized management using just a DHCP server
On the other hand, the downside is that if the DHCP server goes down and cannot be restored,
all DHCP clients may be unable to communicate. This
is a huge problem, but it is a rare accident, so it may not be something to worry about too much.
summary
What did you think?
You may not be familiar with DHCP, but I'm sure most home PCs are set up with DHCP.
Our company also uses DHCP to assign IP addresses to each client.
DHCP is a convenient solution, but if you don't carefully decide how to configure it during the setup phase, you may end up with a lot of trouble.
If the IP address isn't returned even after the lease period has expired, you may end up with a shortage of IP addresses
and end up with a lot of angry users.
Please use it in a planned manner
If you want to talk to a cloud professional
Since our founding, Beyond has used the technical capabilities we have cultivated as a multi-cloud integrator and managed service provider (MSP) to design, build, and migrate systems using a variety of cloud/server platforms, including AWS, GCP, Azure, and Oracle Cloud
We provide a custom-made cloud/server environment optimized for our customers based on the specifications and functions of the systems and applications they require, so if you are interested in the cloud, please feel free to contact us
● Cloud / Server design and construction
● Cloud / Server migration
● Cloud / Server operation, maintenance and monitoring (24 hours a day, 365 days a year)

 0
0






