Uploading and downloading to S3 using "AWS SDK for PHP v3"

table of contents
Hello,
I'm Mandai, the Wild Team member of the development team.
You can find plenty of "AWS SDK for PHP" topics by Googling, but there are still many articles about v2, and the command system has changed significantly, so even if you copy it exactly as it is, it doesn't work properly. (That's me!)
This time, we will provide you with a sample of uploading and downloading to S3 using the "AWS SDK for PHP v3"
Menu
AWS settings
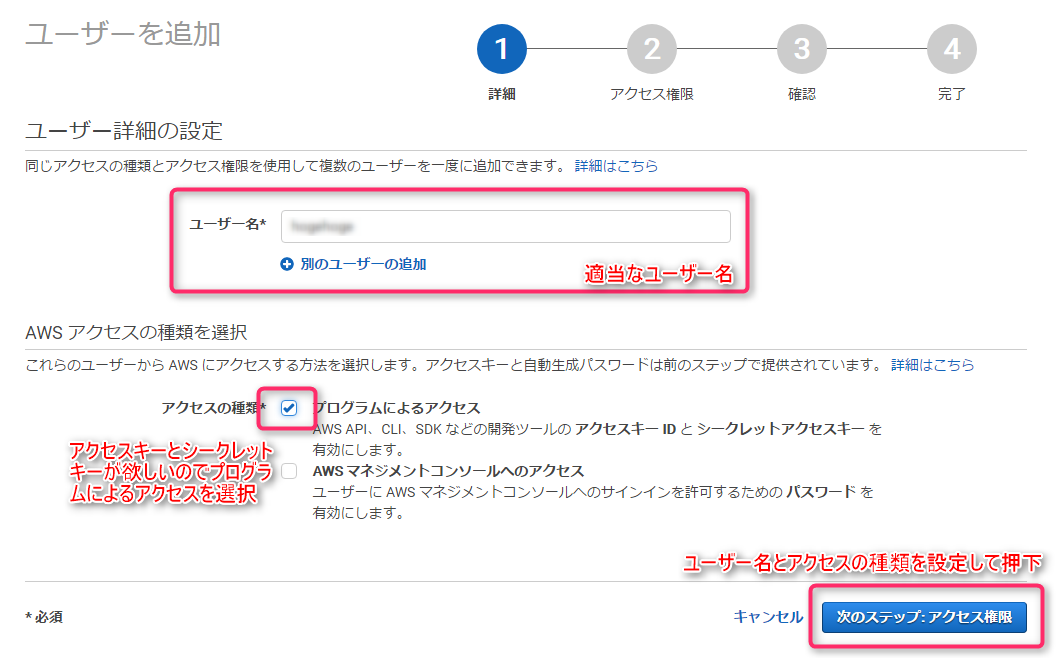
First, before we start writing the code, we will configure the AWS side. We will
create an S3 bucket and optionally set up a dedicated IAM for security reasons.
Creating an S3 bucket
the S3 page, start creating a bucket by clicking the "Create Bucket" button.
Name and Region
Bucket Name
The bucket name is also listed on the screen, and it says to "Enter a DNS-compliant bucket name."
DNS compliance means
- Consists of alphanumeric characters, hyphens, and periods only (underscores cannot be used)
- The number of characters must be between 3 and 63
- Does not end with a hyphen or dot
- Hyphens and dots cannot occur next to each other ('.-', '-.')
- No consecutive dots ('..', '...')
- The first character must be an alphanumeric character
It's something like this
If you separate characters with a dot, an SSL certificate warning will occur when using a subdomain format for SSL communication. It
is best to avoid using dots as much as possible.
Region
For Region, select the region you want to store your data in.
If you are using a service for Japan, it is best to select "ap-northeast-1" (Tokyo).
Copy the configuration from an existing bucket
If you want to use the same settings as other buckets, select them here
Setting properties
You can create a bucket by setting the name and region, but you can also use S3 more intelligently by enabling features such as access control, version control, and logging
Versioning
Ensure uploaded files are versioned
Logging
This setting outputs access history to a log.
The function itself is free to use, but since the log files are stored in S3, S3 storage fees will naturally be charged.
Also, if you view the log, data transfer fees will be charged.
Tags
You can set tags linked to billing information.
Using this feature, you can create separate bills for S3 object usage fees set within the same account.
Setting Permissions
You can set who can access it and the scope of its availability
Manage Users
Set the user who can operate the bucket.
This user is linked to your AWS account and must be created in IAM.
Manage public access permissions
The case where you would check "Read by everyone" is when storing static files on your site.
For buckets where you plan to store PDFs containing personal information or important Excel spreadsheets, do not check the "Public Access" item.
As we will see later, if you are generating a time-limited URL, you do not need to set public access permissions, so don't worry about that
This completes the creation of the S3 bucket
IAM configuration
To access from PHP, you need to write the access key and secret key in the source code configuration file.
It's not a good idea to set an access key that can do anything, so create a user that can only access the S3 bucket you set up this time, and use that user to perform operations on S3.
First, open the IAM user creation screen and enter the following:
You will set access permissions in the next step, but for now, proceed to the confirmation screen without setting anything.
A warning message will appear saying "This user does not have access permissions," but ignore it and click the "Create User" button to complete the creation.
A CSV file containing the access information will be sent to you by email. Alternatively, you can download the CSV file by clicking the download button on the screen and keep it handy
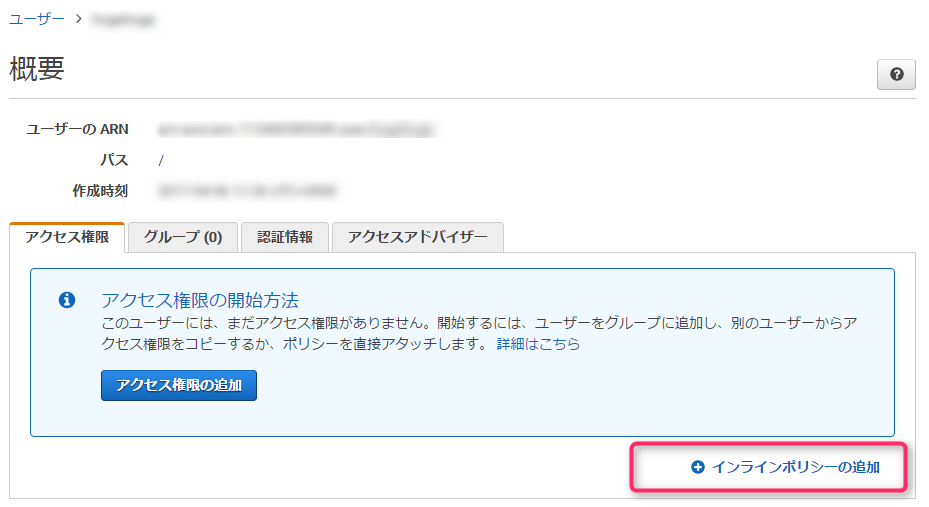
Next, from the user list, click on the username you just created to display the overview page
Start by setting up the policy by clicking "Add inline policy."
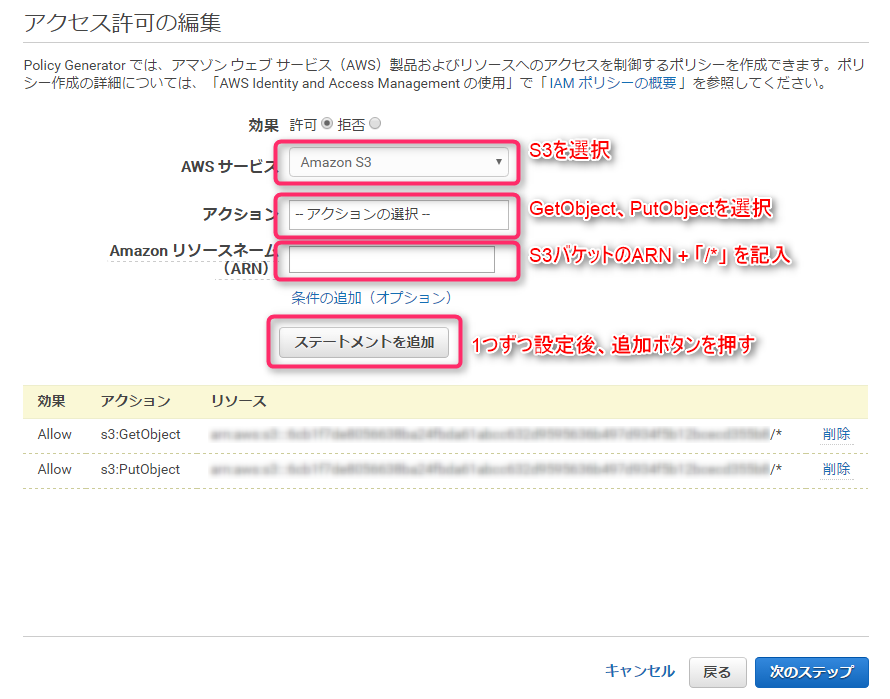
- Select "Amazon S3" as the AWS service
- Actions include GetObject
- Enter the S3 bucket ARN followed by "/*" in the Amazon Resource Name field
- When you register the "Add Statement" button, it will be added below
Repeat the above steps for "PutObject" and add the two statements shown in the image below
Once you're done, click the "Next Step" button to proceed to the confirmation screen
Give the policy a name that is easy to understand, and check the policy (this should be fine, but you should check the ARN)
Click Validate Policy and when you see the message "This policy is valid," click Apply Policy to complete the process
PHP preparation
Now we are finally ready to write some PHP code, but we need to install the "AWS SDK for PHP"
This time I installed it using composer, so I will show you the steps
If you are using a clean environment, simply run the install command and you're done
composer install aws/aws-sdk-php
If your environment has already been set up via composer, you don't need to modify composer.json; instead, use the subcommand called require
composer require aws/aws-sdk-php
You now have the latest AWS SDK for PHP installed
Upload process (local → S3)
To access S3 from PHP, use the S3Client class
# Pattern for creating a client object from the S3Client class $s3client = new Aws\S3\S3Client([ 'credentials' => [ 'key' => 'your access key', 'secret' => 'your access secret', ], 'region' => 'ap-northeast-1', 'version' => 'latest', ]); # Pattern for creating a client object from the factory() method of the S3Client class $s3client = S3Client::factory([ 'credentials' => [ 'key' => 'your access key', 'secret' => 'your access secret', ], 'region' => 'ap-northeast-1', 'version' => 'latest', ]);
There are two ways to create a client object, both of which are treated the same
Next, we will perform the actual upload process.
We will use the putObject() method.
$result = $s3client->putObject([ 'Bucket' => 'your bucket name', 'Key' => 'file key', 'SourceFile' => '/path/to/file', 'ContentType' => mime_content_type('/path/to/file'), ]);
If the upload is successful, $result will return an Aws\Result class,
which contains information about the S3 object you created.
Download process (S3 → local)
Now, let's try downloading it instead
First, create an S3 client
$s3client = new Aws\S3\S3Client([ 'credentials' => [ 'key' => 'your access key', 'secret' => 'your access secret', ], 'region' => 'ap-northeast-1', 'version' => 'latest', ]);
Then, as you might guess, we get the file using the getObject() method
$result = $s3client->getObject([ 'Bucket' => 'your bucket name', 'Key' => 'bucket key', ]);
If the download is successful, an Aws\Result class will be returned in $result
Generate expired URLs
S3 allows you to create a URL with a download setting,
which allows you to download important files without making them publicly available.
This is a feature that is also used by ChatWork, and files uploaded to chat groups can be downloaded using this mechanism
This implementation is also very simple, and although the steps are slightly different, it is done in the same way via S3client
$cmd = $s3client->getCommand('GetObject', [ 'Bucket' => \Config::get('file.s3.bucket'), 'Key' => $file->path, ]); $result = $s3client->createPresignedRequest($cmd, '+30 seconds');
The getCommand() method converts the behavior of the getObject() process into a command and passes it to the createPresignedRequest() method
The second argument of the createPresignedRequest() method can be set to three types: Datetime class, timestamp, or a string that can be interpreted by the strtotime() function
Also, the expiration date cannot be set to more than one week, and the maximum is one week
If you access a link that has expired, the following screen will be displayed and you will not be able to access the object
summary
The AWS SDK for PHP is easy to install and has an easy-to-use class system, but there are inevitably differences between versions, such as missing methods or different arguments, so I hope this article will be helpful in your development
That's all

 2
2