How to check server load with load average and Linux process explained

table of contents
My name is Ito and I'm an infrastructure engineer.
One of the biggest concerns in server operation and maintenance is a sudden increase in load.
"The service is slow, but I don't know why!"
, I'd like to explain what "load average" is, which is often the first thing you check.
About load average
When the load is high and a website or game is slow, the first thing you should do is use the top command.
The top command displays the current status of the OS in real time.
There is a lot of information, so you may not know where to start.
This time we are talking about load average, so let's check the load average
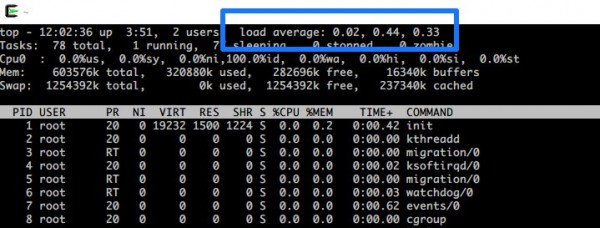
Load Average (LA) represents the "queue of processes" for the server and is typically displayed as an average value over periods such as 1 minute, 5 minutes, or 15 minutes
In the diagram above, from left to right, it shows "LA 1 minute ago," "LA 5 minutes ago," and "LA 15 minutes ago."
that various processes are requesting the CPU to process them, but the server cannot handle them all, so
the processes are queuing up behind.
The higher the load average, the more heavily loaded the server is
The number of processes a server can process at one time is equal to the number of CPU cores on the server.
Multitasking is possible, so for example, a four-core server can process four processes at once.
About Linux processes
Do you now have a rough understanding of load average?
Now let's talk about Linux processes, which also have different states
| TASK_RUNNING | The process is in a state where it can be executed, and is either running or waiting to be executed |
|---|---|
| TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE | Interrupts are possible, but it is unclear when the process will return, such as when waiting for user input |
| TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE | The server is overloaded and cannot be interrupted, so it is waiting |
| TASK_STOPPED | Aborted state |
| TASK_ZOMBIE | So-called zombie processes |
Reference: Process Management 1 - Process Descriptor - Pridact Information Sharing Wiki
Reference: Learn How Linux Works - Process Management and Scheduling
Of these, the following three are not load-related conditions:
- TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE: This task is waiting for user input, so it is not queued because it is not known when it will return
- TASK_STOPPED: The process is stopped
- TASK_ZONBIE: Turned into a zombie
In other words, the remaining two are queued and become the load average value, which is the "system load." This can be "
task waiting to run (TASK_RUNNING)" or "high load and cannot be interrupted (TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE)."
- TASK_RUNNING
- TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE
Other commands that LA can check
Here are two other commands that can be used to check the load average
The w command allows you to see what other users are logged in
[root@test ~]# w 12:49:13 up 4:38, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT vagrant pts/0 10.0.2.2 11:43 0.00s 0.00s 0.00s sshd: vagrant [priv] vagrant pts/1 10.0.2.2 11:55 54:08 2.06s 0.00s sshd: vagrant [priv]
The uptime command allows you to check how long your server will continue to operate.
You can also check the load average here.
[root@test ~]# uptime 12:49:34 up 4:38, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
summary
So, this time I explained about load average!
- Check the load average when the load is high
- Find out how many processes your server can't handle
- The higher the load average, the higher the load
- Although it is called a "process," there are various states
- There are several commands to view the load average
It would be great if we could create a system that didn't require us to worry about such things, but it's still very important to know these values when operating a server, so make sure you understand them properly!
If you want to talk to a cloud professional
Since our founding, Beyond has used the technical capabilities we have cultivated as a multi-cloud integrator and managed service provider (MSP) to design, build, and migrate systems using a variety of cloud/server platforms, including AWS, GCP, Azure, and Oracle Cloud
We provide a custom-made cloud/server environment optimized for our customers based on the specifications and functions of the systems and applications they require, so if you are interested in the cloud, please feel free to contact us
● Cloud / Server design and construction
● Cloud / Server migration
● Cloud / Server operation, maintenance and monitoring (24 hours a day, 365 days a year)

 1
1






