Try Amazon CloudWatch Logs

table of contents
I'm Sashihara, an infrastructure engineer!
AWS offers a service called CloudWatch that monitors things like CPU usage.
CloudWatch has a variety of functions, but this time I decided to try out CloudWatch Logs, which I was particularly interested in.
What are CloudWatch Logs?
This is a service that can monitor log files for EC2 and other applications and generate alarms when specific strings are found
Log File Monitoring - Amazon CloudWatch
For now, I'll try to send the Apache access logs on EC2
Creating an IAM role
Create an IAM role to send log files to CloudWatch Logs
Since we will be sending log files from EC2, select Amazon EC2 as the role type
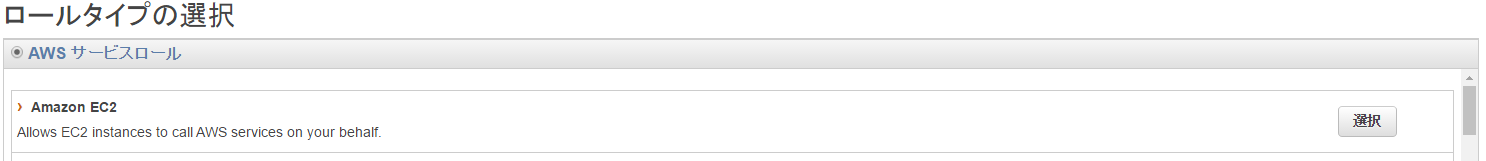
A CloudWatch Logs policy is available, so we will use this this time
Select CloudWatch logs Full Access
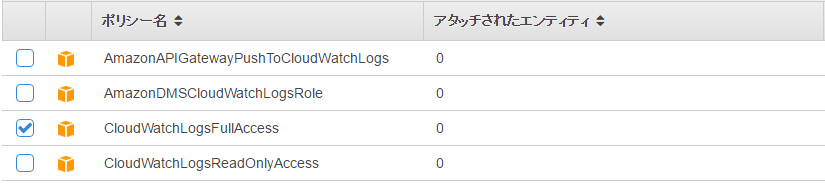
This is all you need to configure for IAM
Then create an EC2 instance with the IAM role assigned
Installing awslogs
After logging in to the launched instance, install the dedicated agent awslogs
[ec2-user@ip-172-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]$ sudo yum install awslog
Next, we will change the configuration file.
The default setting uses CloudWatch in the Northern Virginia region (us-east-1), so we will change it to the Tokyo region (ap-northeast-1).
[ec2-user@ip-172-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]$ sudo vim /etc/awslogs/awscli.conf [default] region = us-east-1 ⇒region = ap-northeast-1
Configure the agent startup and automatic startup settings
[ec2-user@ip-172-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]$ sudo /etc/init.d/awslogs start Starting awslogs: [ OK ]
Auto-start settings
[ec2-user@ip-172-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]$ sudo chkconfig awslogs on
It should now be sent!
Let's check!
Checking log transmission
If you check on the console, you will see that a log group called "/var/log/messages" has been created
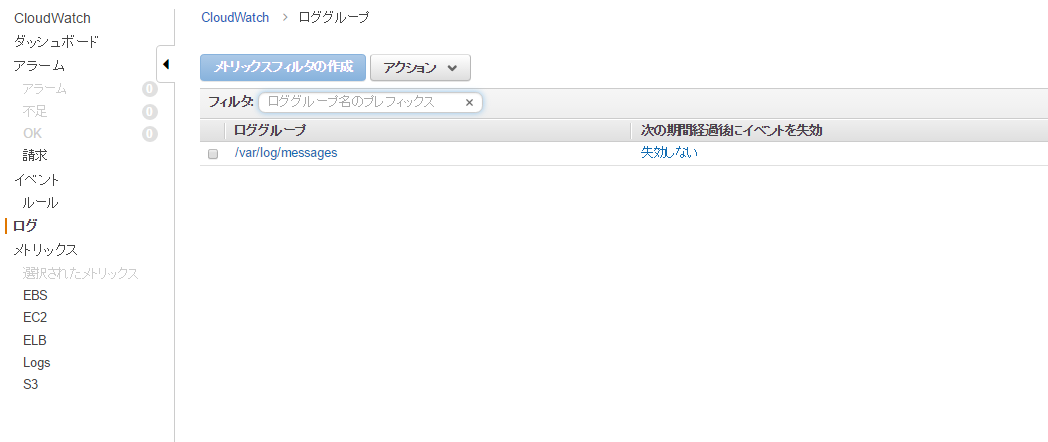
When you click it, the instance ID will be output to the log stream
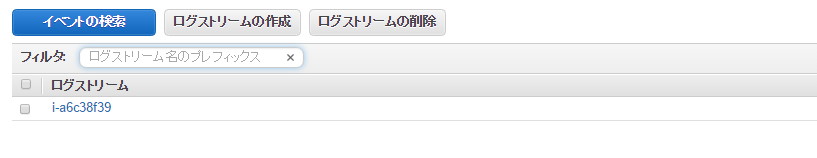
Click on this to see the message contents
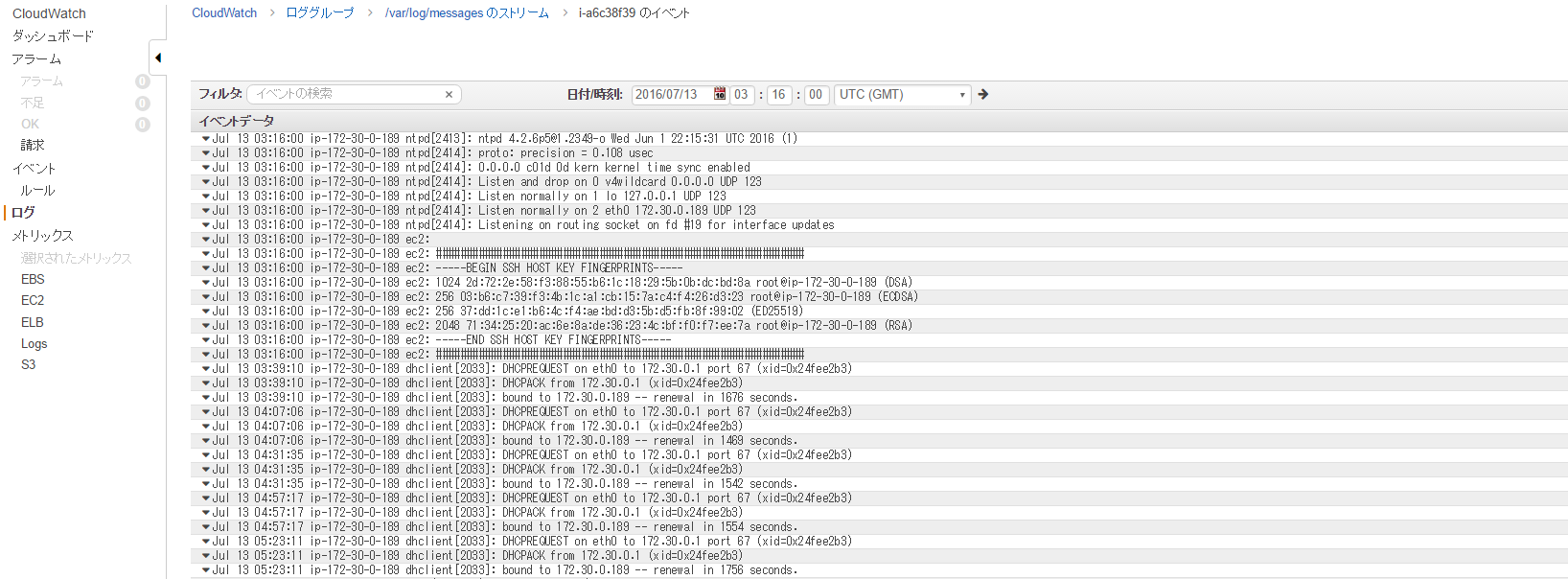
You did it!
Why are messages being written to CloudWatch Logs?
⇒This is because messages is set by default
The configuration is written in /etc/awslogs/awslogs.conf
[/var/log/messages] datetime_format = %b %d %H:%M:%S file = /var/log/messages buffer_duration = 5000 log_stream_name = {instance_id} initial_position = start_of_file log_group_name = /var/log/messages
Send Apache access logs
Now let's try outputting Apache access logs to CloudWatch Logs!
Modify the configuration file on the server
[ec2-user@ip-172-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]$ sudo vim /etc/awslogs/awslogs.conf
The following will be added
[/var/log/httpd/] file = /var/log/httpd/access_log buffer_duration = 5000 log_stream_name = {hostname} initial_position = start_of_file log_group_name = /var/log/httpd
The above settings are as follows
file
Specify the log files to push to CloudWatch Logs (wildcards are allowed, such as /var/log/httpd/*)
buffer_duration
Specify the batch period for log events (5000 is the minimum and default)
log_stream_name
Log stream settings (default is instance_id, but this time we will try hostname)
initial_position
You can also specify the data read position, end_of_file, but the default start_of_file is generally fine
log_group_name
Specify the destination log group
Restart awslogs for the settings to take effect
[ec2-user@ip-172-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]$ sudo /etc/init.d/awslogs restart
Checking log transmission
Let's check it now!!
Check again from the console...
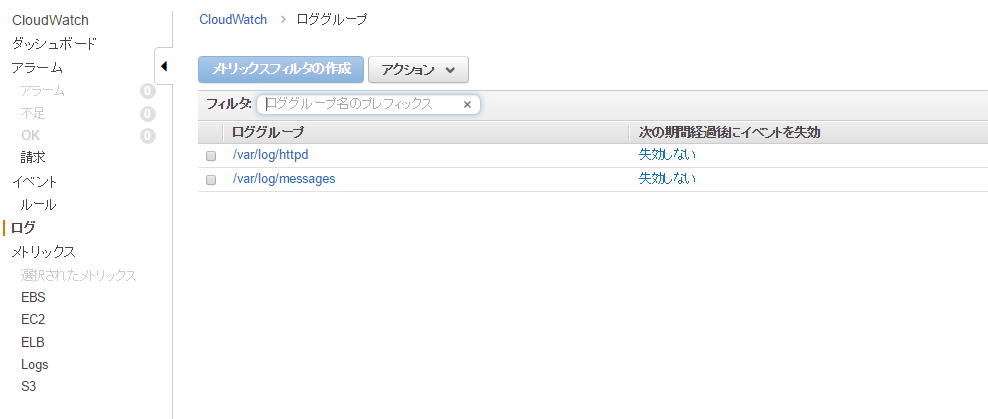
"/var/log/httpd" has been added!
Click on it again...
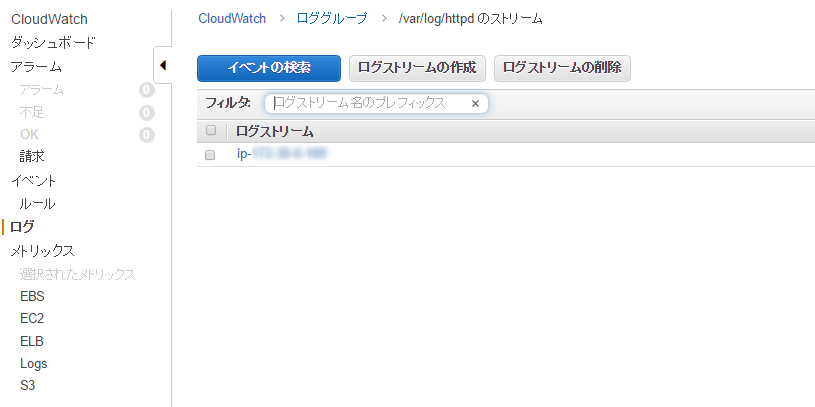
A log stream has been created with the hostname!
I was also able to check the Apache access log!
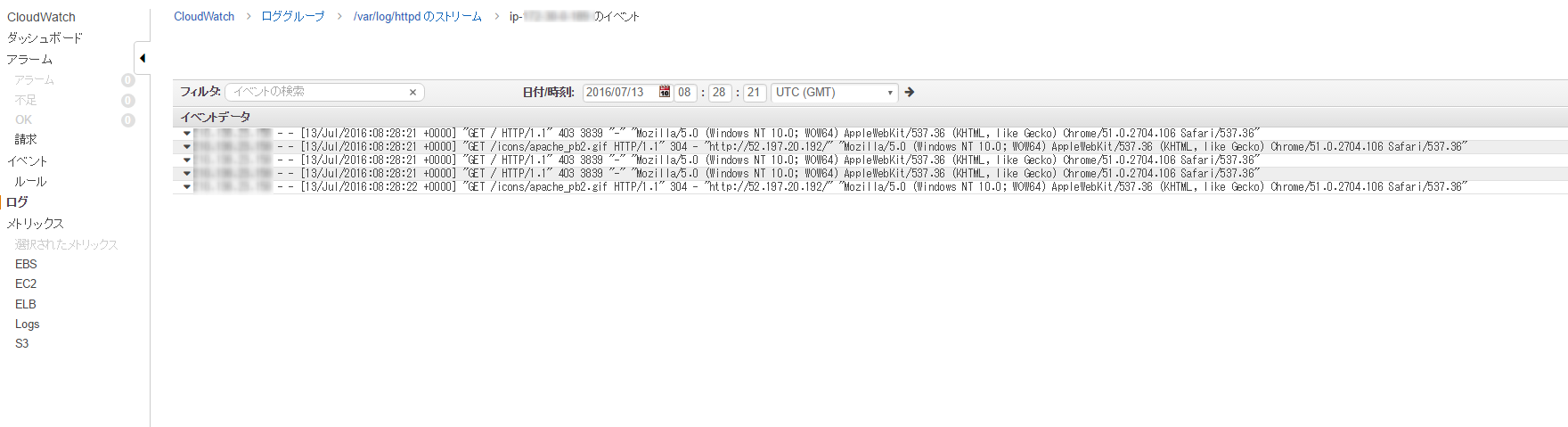
That was easy!
This time we only sent Apache access logs, but it is also possible to monitor HTTP status codes and send an alarm when a 40x error occurs.
You can also use it in conjunction with ElasticSearch to analyze logs
summary
- CloudWatch Logs is a log collection service
- The awslogs agent is useful for this purpose
- It's super easy to just send
Next, we will try to create a serverless architecture using AWS Lambda, which is currently a hot topic!

 0
0






