Introducing features and useful functions you should know when considering using Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB for POLARDB

table of contents
I'm Teraoka, an infrastructure engineer.
This time I'd like to talk about a certain service on Alibaba Cloud.
Alibaba Cloud launches new services in Japan, including cloud database "ApsaraDB for PolarDB"
On the 20th, Alibaba Cloud announced that it will begin offering the relational database "ApsaraDB for PolarDB" in Japan on its public cloud, "Alibaba Cloud."
It's finally here..
So, this time we would like to make full use of PolarDB in the Japan region, and
introduce some useful features that will help you use it as a database for your service!
What is ApsaraDB for PolarDB?
First, let me briefly touch on PolarDB.
PolarDB is a managed relational database service compatible with MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
Developed independently by Alibaba, it is touted as the next generation of managed distributed RDS, and
is capable of delivering high performance and cost-effectiveness.
As you can see when you actually use it,
it is designed with AWS Aurora in mind as a rival to other cloud services
, and Intel's tests have
shown that it has improved QPS by approximately 1.3 times and 95th percentile latency (delay) by approximately 1.8 times compared to Amazon Aurora. *1
If you're thinking about Aurora, you're probably wondering about its features and how it differentiates itself.
I'd like to summarize them by comparing them.
Features of PolarDB and its differences from Aurora
architecture
Both PolarDB and Aurora are called distributed relational database services.
The following is an architectural diagram of PolerDB, which can be roughly divided into four concepts. *2
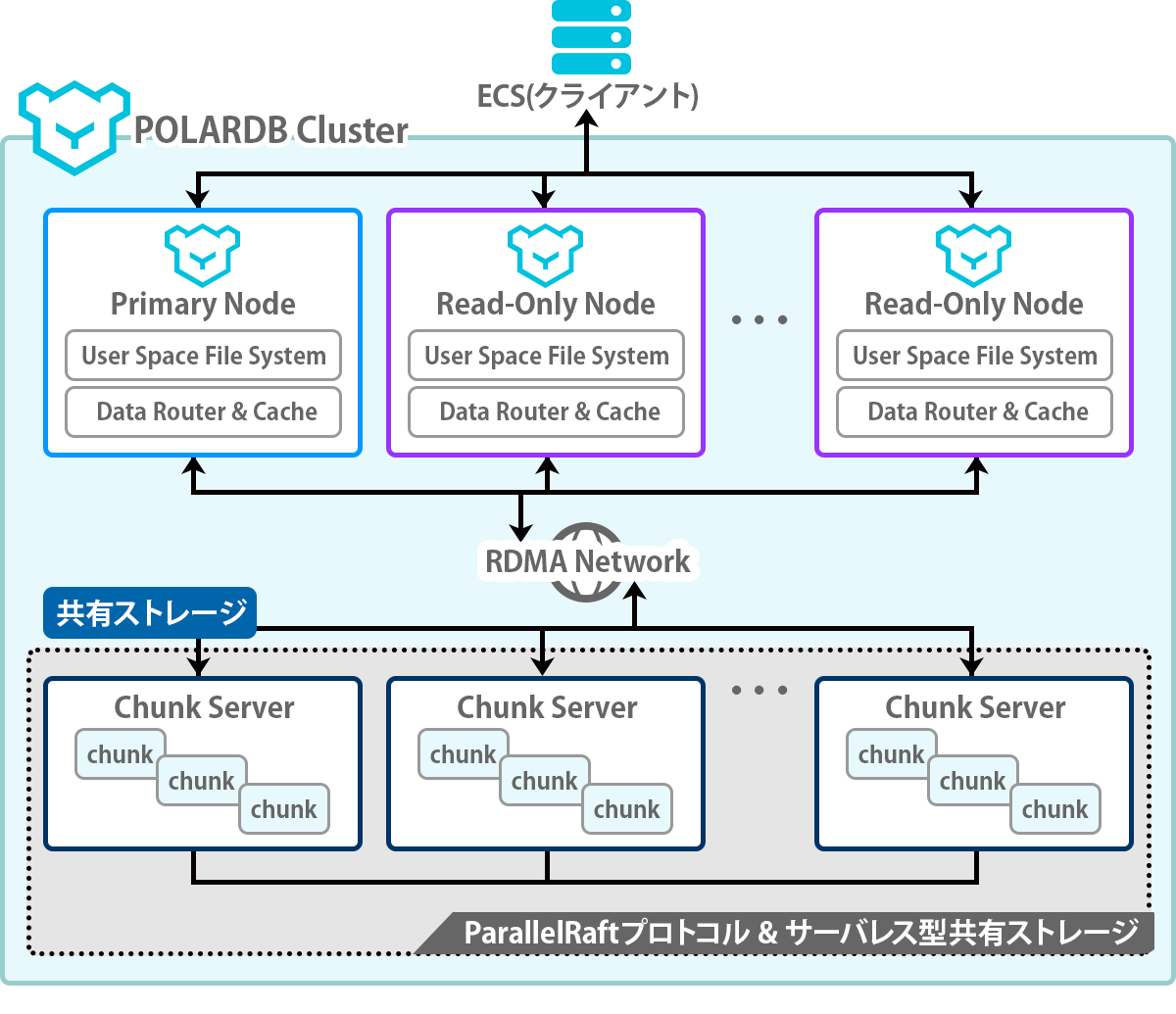
Cluster
It is like a logical group consisting of one Primary Node and N Read-Only Nodes, and
when a Cluster is created, a DNS record called a Cluster Endpoint is automatically assigned.
By accessing this endpoint, you can issue SQL to the DB.
Additionally, PolarDB endpoints support read/write isolation※3
- Write request: sent to the Primary Node
- Read requests: sent to the primary or read-only node depending on the load of each node
In this way, the node to connect to is automatically determined internally.
Aurora has separate endpoints for writing and reading, but
PolarDB only has one and distributes data appropriately internally, which is convenient.
Primary Node
This is the only node in a cluster that can perform both writes and reads.
Write requests to the database are generally executed on this node.
Aurora has a multi-master feature that allows multiple primary nodes to be used, but
PolarDB does not have this feature, so write requests cannot currently be distributed across multiple nodes.
Read-Only Node
These are read-only nodes that can be started up to 15 times within a cluster.
While it is possible to increase or decrease the number manually, by utilizing DAS (Database Autonomous Service)
it is possible to scale in/out depending on the load situation. *4
The AutoScall function and the ability to start up to 15 units are the same as Aurora, so
it is clear that they have taken great care in terms of functionality.
Chunk Server
Both PolarDB and Aurora completely separate the computing and storage processes of each node.
Storage processing in PolarDB is handled by something called a Chunk Server.
DB data is stored on this Chunk Server, and
it is possible to automatically scale up and down storage capacity according to the amount of data.
Aurora also has automatic storage scaling, but the maximum expansion capacity is different:
Aurora can expand up to 64TB, while PolarDB can expand up to 100TB.
Useful features of PolarDB
Here are some of the features I found useful when actually using it
Data migration support by DTS
If you are using PolarDB for the first time, you do not need to consider this, but
if you are switching from an existing service's database, you will need to consider the following.
- How to migrate data from an existing database
- How to reduce downtime when switching to PolarDB
In such cases, PolarDB allows you to use DTS (Data Transmission Service), so
I think it's great that they have a path for data transfer. *5
Online scale up/down
PolarDB can scale up and down while online, which is probably
the biggest differentiator compared to Aurora, which requires nodes to be temporarily shut down.
I was concerned about the downtime when changing the specifications, so I created a test database like the one below
CERATE DATABASE TEST; CREATE TABLE test ( column int(10) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB;
When changing the specifications, I checked by issuing an update every second
update test set column=unix_timestamp();
The console displays a message stating that you will be unable to connect for up to 30 seconds, but
the total time it took to complete the change process was 10 minutes, and the connection error only occurred for about 10 seconds of that time.
On the other hand, Aurora requires stopping a node when changing specifications, which
results in a downtime of approximately 5 to 10 minutes.
To avoid this, a common practice is
to select the desired specifications in Aurora, add a new read-only node, and
manually fail over that node to promote it to a write node, thereby
minimizing downtime.
Even when using failover, it still takes more than 10 seconds, so
I think PolarDB is definitely faster.
It looks like you could choose to tolerate downtime of around 10 seconds!
Enhancement of monitoring items
PolarDB has a wide range
*6 This is great because you can check not only resources such as CPU but also performance metrics related to InnoDB.
In the case of Aurora, you can check similar metrics in Performance Insights, but there is an additional charge.
PolarDB does not have ※7
You can also use CloudMonitor to set up alerts.
Actually, CloudMonitor is also free to use, which is great!
summary
This article introduced the features and useful functions of PolarDB from an operational perspective.
While the actual setup procedures are not included in this article, it
is important to understand its features and functions when using it for a new project or switching from another RDB, so
I hope this article will be helpful to those considering using PolarDB.
I will also be keeping an eye on future updates to PolarDB.
source
*1 https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/docs/storage/alibaba-cloud-polardb-solution-brief.html
*2 https://www.sbcloud.co.jp/entry/sol/polardb/
*3 https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/ja/doc-detail/68510.htm
*4 https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/doc-detail/169686.htm
*5 https://jp.alibabacloud.com/product/data-transmission-service
*6 https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/ja/doc-detail/68555.htm
*7 https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/ja/doc-detail/68498.htm

 1
1






