Strengthen and better manage your Linux security with aide!

table of contents
Security has been a hot topic for quite some time now, especially in this digital age in Japan where many people are inevitably exposed to systems
I am a Linux server management engineer, and Linux is my favorite OS. Every OS has its advantages and disadvantages, but I like Linux because I find it easy to use
However, while even beginners can manage Linux, it also allows for freedom and allows anyone to create their own best practices. Also, because each person's learning experience varies slightly, it is impossible to manage a system in exactly the same way
In a production environment, there is a high probability that the system is not run by a single person, but is usually managed by multiple engineers. As a Linux administrator, everyone has their own "best practices" and "rules," but the way Linux is used and its specifications vary depending on the system's purpose, environment, and various other aspects
In such a situation..
- "Just write the settings somewhere!"
- "You can't change it at all!"
- Ask permission before making any changes!
- "Who changed it?"
- others!
Managing Linux can seem like a difficult task, but AIDE is a useful tool!
What is aide?
In Europe and the United States, CIS , which is managed by the security community and provides benchmark data for various systems. It provides detailed benchmarks of best practices for operating systems and even middleware.
Especially for those who manage server-based operating systems, there are a wide variety of server types and server configurations, so using benchmark data as a baseline for security enhancements that you are not aware of will undoubtedly only produce positive results
In Linux documentation, you will often find that the use of a tool called AIDE is recommended
aide is a file tamper detection tool called Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment
It is an important tool, especially used by the Pentagon
When you edit a file, the file's SHA changes, so AIDE, which runs on cron, extracts the SHA of the specified file or all files in the file path, compares them in the AIDE database, and records them
example:
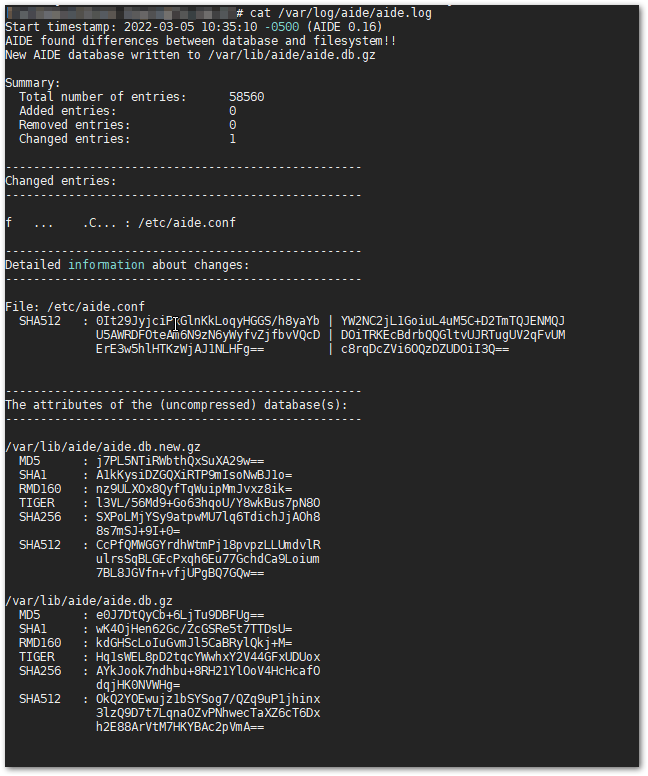
As shown in the image above, you can see which files have changed
Try it out using aide!
1. Install aide!
AIDE is a very useful and necessary tool, so it is available in the standard repositories of Linux distributions such as deb and rhel, making it easy to install
RHEL series
yum install aide
Debian-based
apt install aide
Once installed, check the version!
aide -v
2. Check and edit the aide settings
/etc/aide/aide.conf
or
/etc/aide.conf
There is an AIDE setting in
There are default settings in place at the time of installation, so you can use them as they are
You can also change the configuration files, databases, etc. according to your needs and preferences
3. Initialize aide
RHEL series
aide --init
Debian-based
aideinit
The first time you run it, it will take some time as it records the SHAs of all files in the database
4. Check for tampered files with aide!
RHEL series
aide --check
Debian-based
aide.wrapper --check
Use aide results to manage files
AIDE will tell you which files have changed, and if there is a problem, the normal way is to restore from a backup. However, if you are unable to make a backup, you can use " etckeeper " (explained in another blog) to restore files saved in git.
Can you monitor aide and notify me if anything changes?
/etc/default/aide
The settings for email notifications are described in the
In addition, you can set up a monitoring tool to notify you if it detects an abnormality
This will be a monitoring issue, so I will write about it in my next blog!
Well then!

 6
6






