Starting Wireshark from scratch

table of contents
Hello.
I accidentally echo "" > /etc/passwd. This is Kawa from the System Solutions Department.
I would like to write about Wireshark, which I introduced in a
previous network tools By the way, my favorite shark movie Deep Blue .
What is Wireshark?
This is a well-known tool that is considered essential for network engineers.
It is compatible with Windows and macOS, and basically captures packets on the PC on which it is installed, making it extremely easy to visualize them. It
is often used for network investigations such as troubleshooting.
Download and installation
Click on the file name for the corresponding OS from the "Download" section on
 the official website ( https://www.wireshark.org/
the official website ( https://www.wireshark.org/
Once the download is complete, open the executable file and follow the instructions in the installer, then click "Next."
(The above items are basically OK with the default settings.)
Once the installation is complete, open Wireshark and you'll know it's installed if you see the following screen.
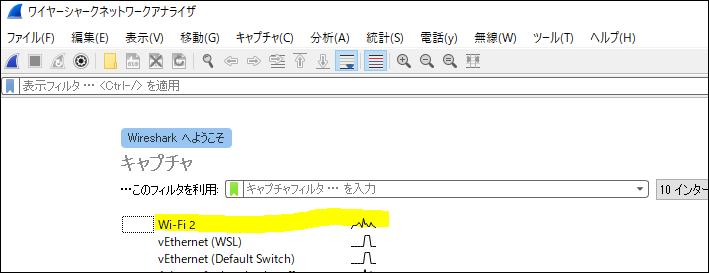
Double-click the network adapter that has a wiggly waveform and take a look at the capture of the main interface you're connected to.
How to view Windows capture data
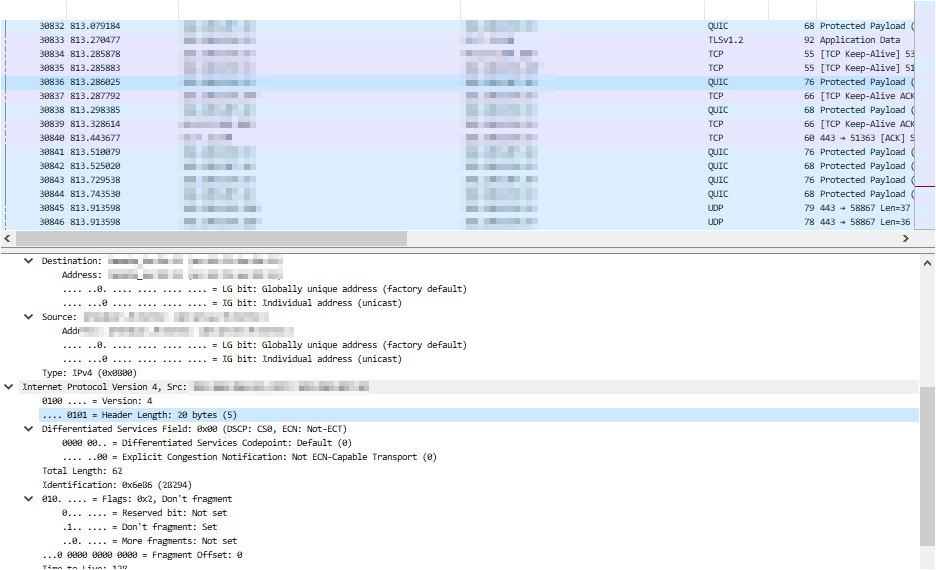
Once you select an interface, the captured inbound/outbound packets will immediately be displayed (IP and other information has been blurred) ⬇
.
Let's try sending a ping to our website (beyondjapan.com) from the command prompt
> ping beyondjapan.com
Enter "icmp" in the search box at the top and press Enter.

Only ping results will be sorted, and you will be able to see ICMP packets addressed to our website.
Right-click on the string at the bottom and select "Expand All" to see the contents of the packet.
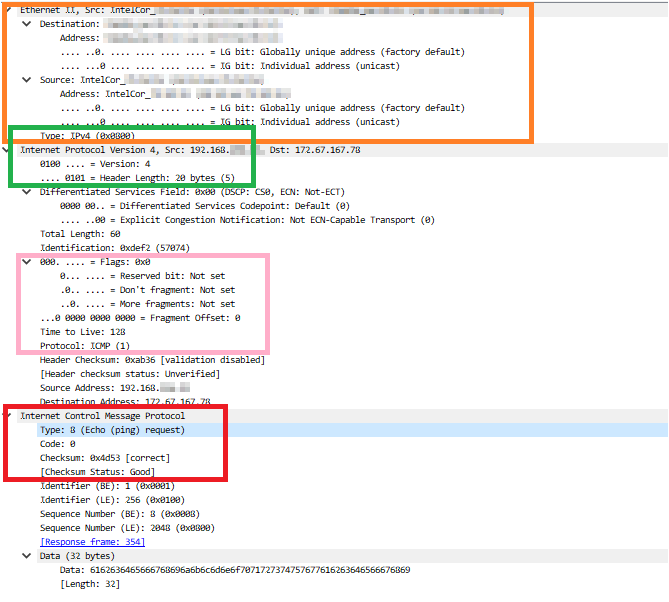
Orange : Source/Destination Address, model and MAC address of the router used, etc.
Green : IP version (v4 and header length in this case)
Pink : Flags, TTL and protocol
Red : ICMP type and checksum
In this case, since it is ICMP, the information available is not very rich, but as long as the packet is not encrypted, you can see detailed data such as the payload (abuse is strictly prohibited)
By the way, if you look at the famous http site of Hiroshi Abe, you can see exactly where you accessed it.
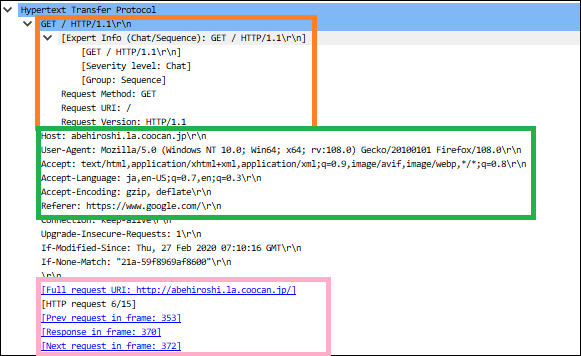
Orange part : Request method and HTTP version
Green part : Host information, browser user agent information, language, referrer, etc.
Pink part : Access URL, frame number related to the series of accesses
On HTTP sites, you need to be especially careful about the information you enter into forms .
If you send a password or other information into a form without encryption, the password string can be seen in a packet capture.
(This is why it's not a good idea to connect to a random Wi-Fi network.)
Filters
To search, we will use Wireshark syntax.
This time, we will introduce some commonly used syntax. Various syntaxes, such as regular expressions, can be used, so it seems like it could also be used for troubleshooting API interactions.
- Filter by IP address
ip.addr == xx.xx.xx.xx !(ip.addr==xx.xx.xx.xx) #Exclude specific IP
Let's try sending a ping to "1.1.1.1" and search for the results.
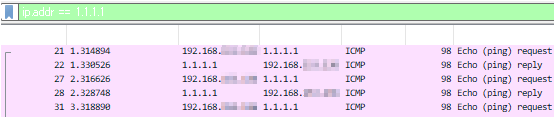
You can see the ping request → reply exchange.
- Filter by port number
tcp.port == xx udp.port == xx tcp.port == xx || udp.port == xx #Multiple searches with or !(tcp.port == xx) #Exclude specific ports !(tcp.port==xx) && ip.addr==xx.xx.xx.xx #And condition
Let's try checking the TCP/443 communication.
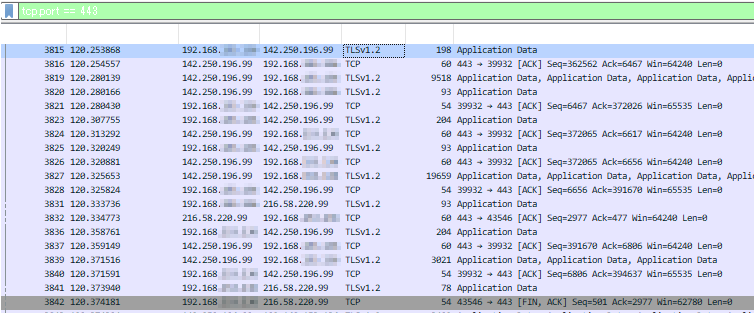
By checking the IP, you can see the flow of a Google search.
By looking at the explanation and flags in the "Info" section, you can see the TCP handshake exchange (ACK, FIN, etc.).
Packet capture on a Linux machine
If you have a PC with Wireshark installed, you can view packet capture files taken on a Linux machine
This time, we will use
tcpdump, which we introduced previously (Please install tcpdump in advance using yum or apt.)
In this article, we will use Ubuntu to create an arbitrary file and output the capture data.
We will write it to a file called "test.pcap" (pcap is the file extension for packet capture files).
*Check and specify the interface name that is missing from the Internet using ifconfig etc.
> tcpdump -i ens33 -w test.pcap
The capture will continue until you cancel it, so generate the communication you want to check while it is being captured (browser access, etc.).
Press "Ctrl+C" to terminate tcpdump and transfer the output file to your Windows/macOS machine.
Open the extracted pcap file in Wireshark to visualize the captured data.

↑We were able to visualize the packets of a beautiful Christmas scan (don't try this at home, kids).
The strength of Wireshark is that anyone can easily capture packet flow as long as they know how to read it
In addition to the PC you are using, you can also capture all packets flowing within the local network by connecting a switch and setting up a mirror port, so this software is often used in the field. It is also a good way to
study TCP/IP, so please try installing it.

 10
10






