Build an ECR with Terraform that scans container images for vulnerabilities when they are pushed

table of contents
My name is Teraoka, and I'm an infrastructure engineer.
In this article, I'll be adding a setting to AWS ECR to scan for vulnerabilities when a container image is pushed.
Since I have the opportunity, I'll try building it using Terraform.
ECR is AWS's managed container image registry.
It stores pushed container images, but
users must be aware of vulnerabilities in the images themselves.
One of the features of ECR is the ability to automatically run vulnerability scans when you push, so
I would like to build a repository with this setting enabled.
Create an ECR repository
We will use the resource aws_ecr_repository
#################### # Provider ################### variable "aws_access_key" { description = "AWS Access Key" } variable "aws_secret_key" { description = "AWS Secret Key" } variable "aws_role_arn" { description = "AWS Role Arn" } variable "aws_region" { default = "ap-northeast-1" } provider "aws" { access_key = "${var.aws_access_key}" secret_key = "${var.aws_secret_key}" region = "${var.aws_region}" assume_role { role_arn = "${var.aws_role_arn}" } } #################### # # ECR ################### resource "aws_ecr_repository" "image-scan-test" { name = "image-scan-test" image_tag_mutability = "MUTABLE" image_scanning_configuration { scan_on_push = true } }
Set scan_on_push to true in the image_scanning_configuration block.
Let's start from the init.
$ terraform init Initializing the backend... Initializing provider plugins... - Checking for available provider plugins... - Downloading plugin for provider "aws" (hashicorp/aws) 2.56.0... The following providers do not have any version constraints in configuration, so the latest version was installed. To prevent automatic upgrades to new major versions that may contain breaking changes, it is recommended to add version = "..." constraints to the corresponding provider blocks in configuration, with the constraint strings suggested below. * provider.aws: version = "~> 2.56" Terraform has been successfully initialized! You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands should now work. If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform, rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
Just to be safe, run the plan before reflecting the changes
$ terraform plan Refreshing Terraform state in-memory prior to plan... The refreshed state will be used to calculate this plan, but will not be persisted to local or remote state storage. --------------------------------------------------------------------------- An execution plan has been generated and is shown below. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: + create Terraform will perform the following actions: # aws_ecr_repository.image-scan-test will be created + resource "aws_ecr_repository" "image-scan-test" { + arn = (known after apply) + id = (known after apply) + image_tag_mutability = "MUTABLE" + name = "image-scan-test" + registry_id = (known after apply) + repository_url = (known after apply) + image_scanning_configuration { + scan_on_push = true } } Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Note: You didn't specify an "-out" parameter to save this plan, so Terraform can't guarantee that exactly these actions will be performed if "terraform apply" is subsequently run.
Click Apply to reflect the changes
$ terraform apply An execution plan has been generated and is shown below. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: + create Terraform will perform the following actions: # aws_ecr_repository.image-scan-test will be created + resource "aws_ecr_repository" "image-scan-test" { + arn = (known after apply) + id = (known after apply) + image_tag_mutability = "MUTABLE" + name = "image-scan-test" + registry_id = (known after apply) + repository_url = (known after apply) + image_scanning_configuration { + scan_on_push = true } } Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. Do you want to perform these actions? Terraform will perform the actions described above. Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve. Enter a value: yes aws_ecr_repository.image-scan-test: Creating... aws_ecr_repository.image-scan-test: Creation complete after 0s [id=image-scan-test] Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed
It has been reflected
Push the container image to ECR
We will use the following image, which, judging from its name, seems to be full of vulnerabilities.
Please pull it locally beforehand.
https://hub.docker.com/r/cved/cve-2019-9978
To push to ECR, simply obtain your authentication information using the aws ecr get-login command and
run the docker push command as usual.
$(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email --region ap-northeast-1 --profile test-profile) $ docker tag cved/cve-2019-9978 XXXXXXXXXXXX.dkr.ecr.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/image-scan-test:latest $ docker push XXXXXXXXXXXX.dkr.ecr.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/image-scan-test:latest
Once pushed, check it from the management console
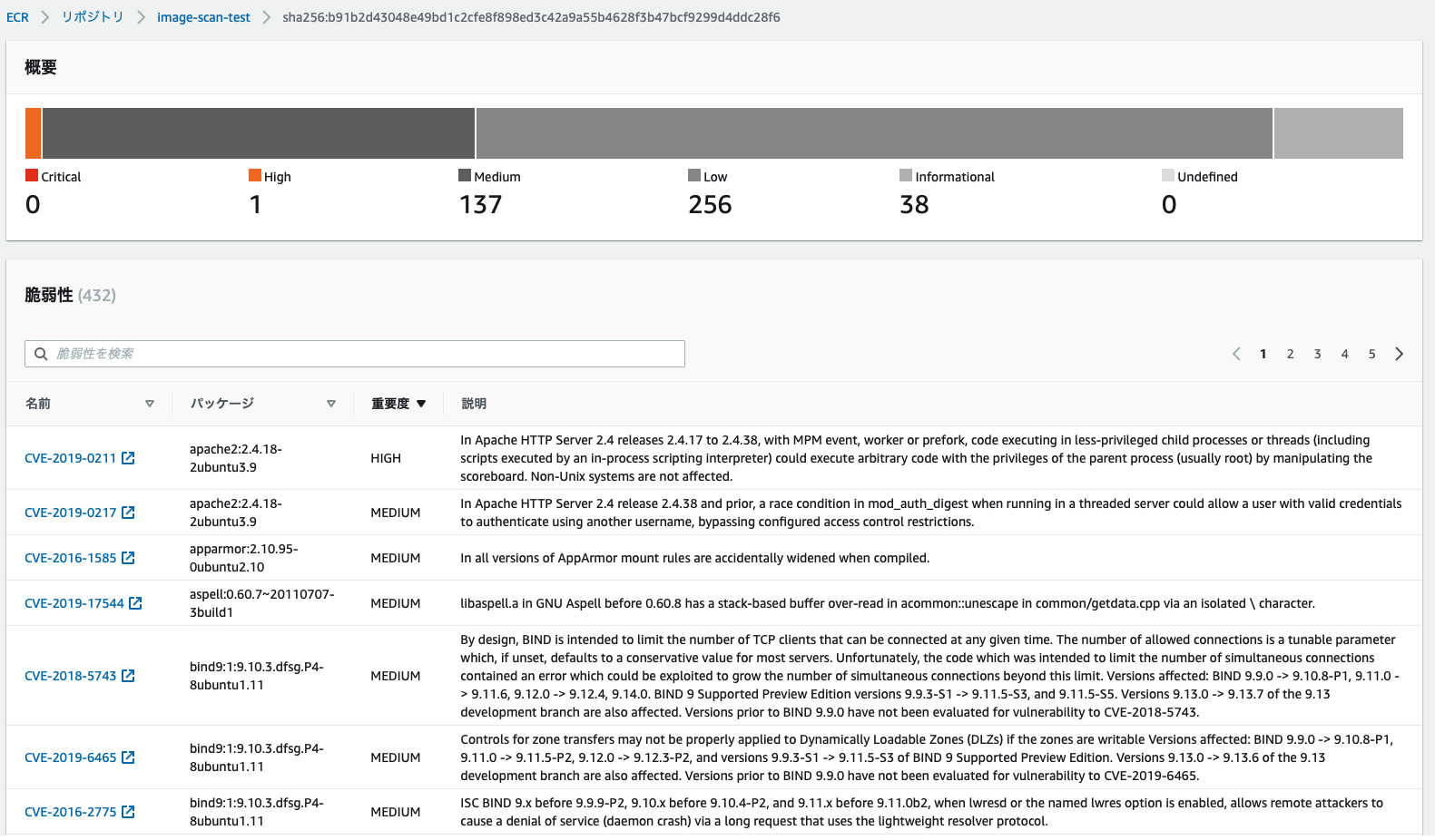
The scan will be performed automatically and you can check the results.
There are so many vulnerabilities, the battle against them is never-ending...
summary
What did you think?
The setup itself is easy, and if you code it in Terraform, it will be easier to deploy later.
I encourage everyone to give it a try.

 1
1






