[Azure] Auto-scaling SQL Database DTUs using Azure Automation

Hello, this is Hase from the System Development Department
I am currently developing a web system using App Service and SQL Database provided by Azure, but before we begin operation, I am considering implementing auto-scaling to reduce costs as much as possible
However, App Service has an auto-scaling feature, but SQL Database does not
I wondered if there was any way to do this, so I did some research and found an article that said that you can autoscale SQL Database by using a feature called Azure Automation
When I actually tested it, auto-scaling worked perfectly, so I would like to introduce how to do it this time
premise
SQL Database has multiple purchasing models (DTU, vCore-based, and serverless), but in this example we will use DTU
What is Azure Automation?
- One of the features of Azure Portal is the ability to automate tasks (called Runbooks in Azure Automation)
- Can be executed periodically by specifying a time (e.g., midnight every day)
- Runbooks can be written in PowerShell, PowerShell Workflow, Python 2, and DSC
Implementation image
- Create a SQL Database scaling runbook in Azure Automation using PowerShell
- Add the created Runbook to a schedule so that the Runbook will be executed automatically at a specified time
procedure
Add an Azure Automation account
① Log in to the Azure Portal
② Select "Automation Account" from Azure Services
③ Select "+Add" to add an Automation account
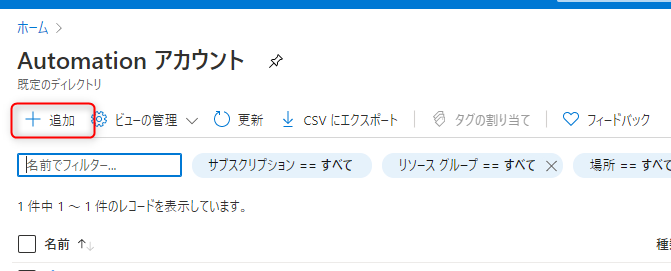
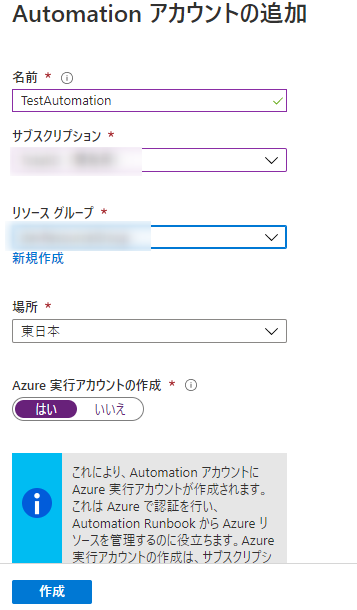
④ Enter your Automation account information and create it
| name | Any name |
|---|---|
| Subscription | Select the subscription you are using |
| Resource Group | Select the resource group you are using |
| place | Server Region |
| Creating an Azure Run As account | Select "Yes" *1 |
 *1) Make sure to select "Yes" for creating an Azure Run As account. ⇒
*1) Make sure to select "Yes" for creating an Azure Run As account. ⇒
In order to operate
SQL Database with a Runbook, approval of the Run As account is required. If you select "No," you will not be able to perform SQL Database operations from the Runbook.
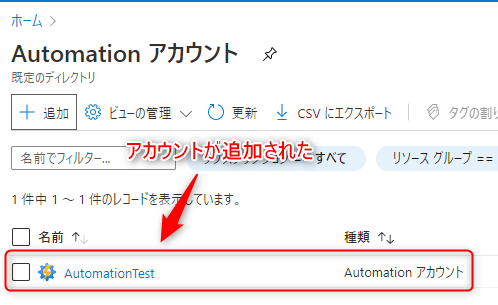
Once created, your Automation account will appear in the list
Add a module to the added Automation account
To operate SQL Database from Runbook (task), add the following module:
| Az.Account | A module to manage all Azure credentials and common configurations |
|---|---|
| Az.Automation | Module that manages information about Azure Automation |
| SqlServer | Module with new cmdlets that support the latest SQL features |
⑤ Modules are configured for each Automation account, so select the account you created
⑥ Select "Module Gallery"
Shared Resources > Module Gallery
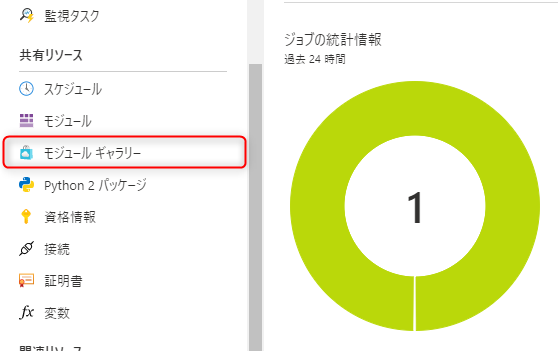
⑦ Install the module you want to register from the module gallery screen
Here we register the Az.Account module (the order of installation does not matter)
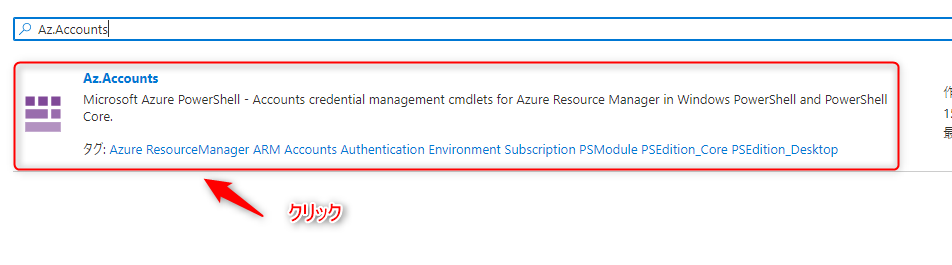
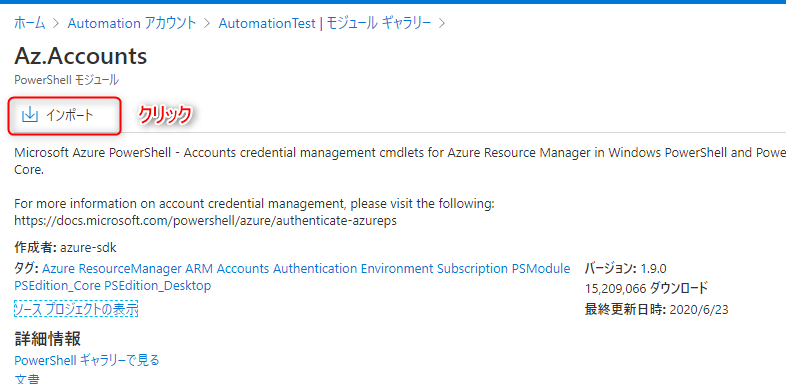
8. The details screen for the Az.Accounts module will be displayed. Click "Import."
9. The import confirmation screen will appear, so click "OK"
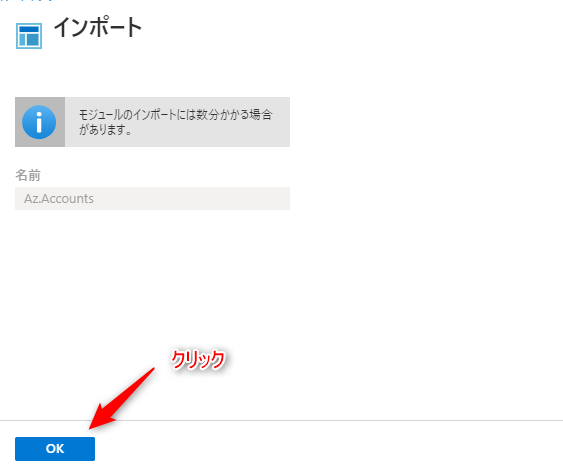
The Az.Accounts module import begins
If the import is successful, the message "Import successful" will be displayed in the upper right corner of the screen
10. Import the remaining modules in the same way
Create a Runbook (Task)
⑪ Select "Runbook" from the Automation account you created
Process Automation > Runbooks
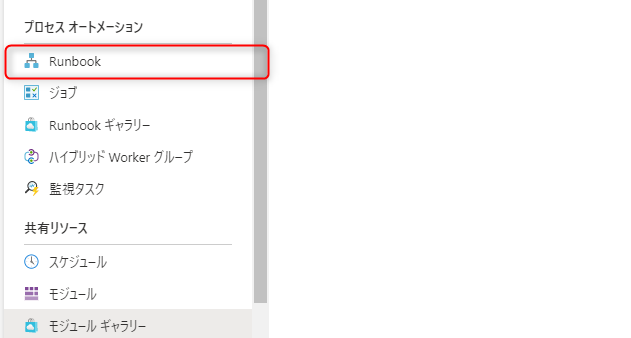
⑫ Select "+ Create Runbook" to create a Runbook
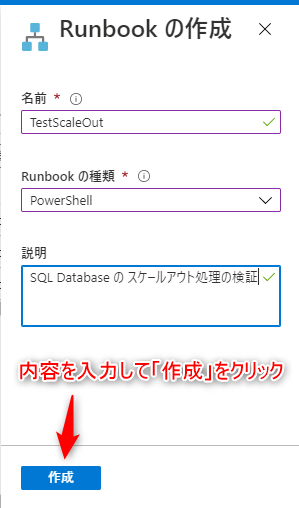
⑬ Enter the Runbook information and create it
| name | Any name |
|---|---|
| Runbook types | PowerShell |
| explanation | Optional description |
The created runbook will be displayed in the list.
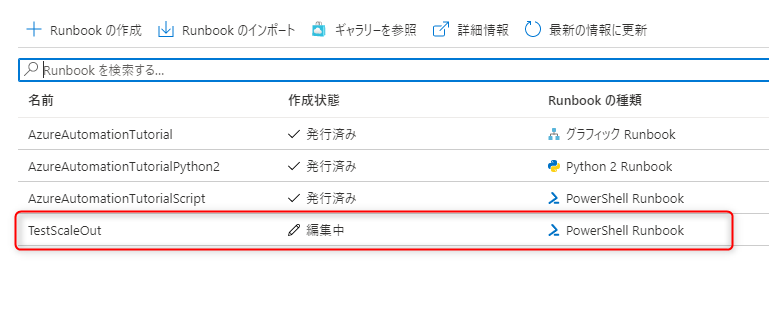
*AzureAutomationTutorial, AzureAutomationTutorialPython2, and AzureAutomationTutorialScript are provided by default when you create an Automation account, so we will not use them this time.
Write code in a runbook
Write the process to execute auto-scaling in the created Runbook.
* PowerShell is used as the language.
■ Rough implementation flow
① Obtain Azure Automation connection information
② Use the obtained Azure Automation connection information to connect to your Azure account
③ Change the SQL Database specifications
※ To change the SQL Database specifications using PowerShell, you must be connected to your Azure account.
⑭ Select the Runbook you created
⑮ Select "Edit" to open the code editor
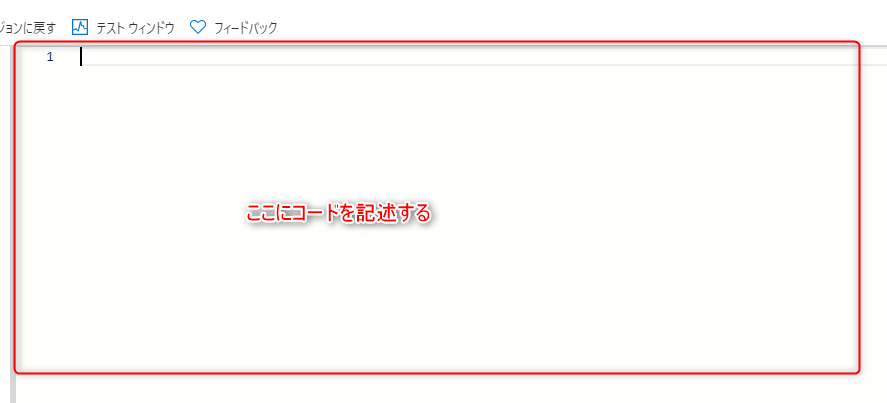
Write the code here
16. Write a process to obtain Azure Automation connection information
■ Code
# Write a command to get Azure Automation connection information and assign it to a variable $connection = Get-AutomationConnection -Name "{Automation account connection name}"
■ Command details
| Get-AutomationConnection | |
|---|---|
| Gets information about Azure Automation connections | |
| option | |
| -Name | Azure Account name to retrieve information for |
⑰ The Automation account connection name in step 21 can be confirmed from "Connections"
Shared Resource > Connections
18. Use the Azure Automation connection information you obtained to connect to your Azure account
■ Code
# Authorize Azure account Connect-AzAccount -Tenant $connection.TenantID ` -ApplicationId $connection.ApplicationID -CertificateThumbprint ` $connection.CertificateThumbprint
* If you want to start a new line in the middle of an expression, add a grave accent (`) at the end
■ Command details
| Connect-AzAccount | |
|---|---|
| Connect to your Azure account | |
| option | |
| -Tenant | Azure Automation tenant ID |
| -ApplicationId | Azure Automation Application ID |
| -Certificate Thumbprint | Azure Automation certificate information |
⑲ Change the SQL Database specifications
■ Code
# Change the SQL Database plan to S0 (Standard DTU 10) Set-AzSqlDatabase -ResourceGroupName "{resource group name}" ` -DatabaseName "{SQL Database name}" -ServerName "{SQL Server name}" ` -Edition "Standard" -RequestedServiceObjectiveName "S0"
■ Command details
| Set-AzSqlDatabase | |
|---|---|
| Set SQL Database properties | |
| option | |
| -ResourceGroupName | The resource group you are using |
| -DatabaseName | The name of the SQL Database to use |
| -ServerName | The name of the SQL Server to use |
| -Edition | The plan you want to change to (Basic, Standard, or Premium) |
| -RequestedServiceObjectiveName | Enter the DTU you want to change (e.g. S1, P2, etc.) |
Completed Code
Combining the above code will result in this
# Write a command to get Azure Automation connection information and assign it to a variable $connection = Get-AutomationConnection -Name "{Automation account connection name}" # Authorize your Azure account Connect-AzAccount -Tenant $connection.TenantID ` -ApplicationId $connection.ApplicationID -CertificateThumbprint ` $connection.CertificateThumbprint # Change the SQL Database plan to S0 (Standard DTU 10) Set-AzSqlDatabase -ResourceGroupName "{resource group name}" ` -DatabaseName "{SQL Database name}" -ServerName "{SQL Server name}" ` -Edition "Standard" -RequestedServiceObjectiveName "S0"
Check the operation of the created Runbook
⑳ Open the test window to check the operation of the created runbook
Select "Test Window" on the code editor screen
21. Select "Start" to run the test
22. If the test is completed successfully, the stream will be displayed
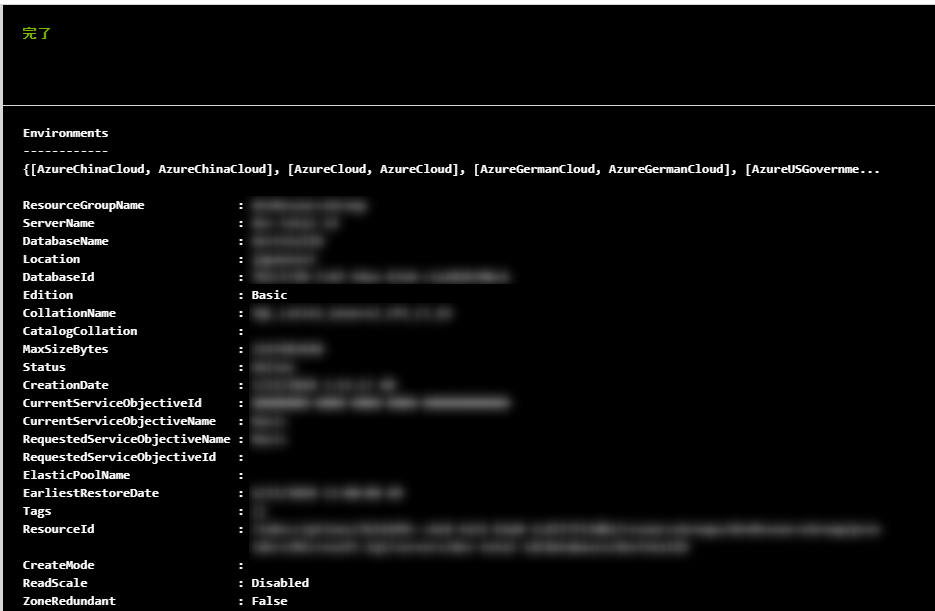
If the test fails, the error will be displayed in red
You can confirm that the plan for the target SQL Database has been changed
Register the created runbook to a schedule
Register the created Runbook in a schedule so that it can be executed periodically.
* To register a Runbook in a schedule, you must publish the Runbook so that it can be used in the production environment.
22) To publish the Runbook, click "Publish" and select "Yes"
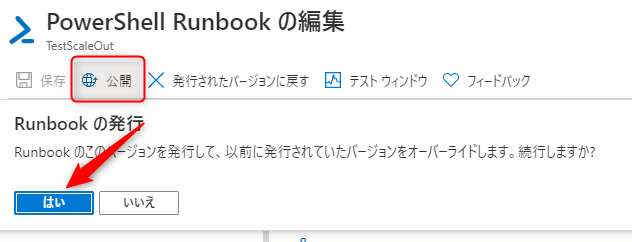
If the runbook is published successfully, a message will appear in the upper right corner of the screen
22. Next, click "Link to Schedule" to register for the schedule
22. The schedule setting screen will appear, so create a new schedule and register it
Schedule > + Create a new schedule.
*No need to create a new schedule if a schedule is already available.
27. Enter the schedule time setting information and click "Create"
| name | Any name |
|---|---|
| explanation | Optional description |
| At the start | Select any start date and time |
| Time Zone | Select your desired time zone |
| repetition | Select either "Once" or "Regularly" |
| interval | Optionally select the execution interval (only if "Repeat" is set to "Periodic") |
| Set expiration date | Select either "Yes" or "No" |
| date of expiry | Optionally select an expiration date and time (only if "Set expiration date" is set to "Yes") |
22. The created schedule will be selected, so click "OK"
If the schedule is registered successfully, a message will be displayed on a blue background
22) When the schedule is executed, it will be displayed in the job list
Process Automation > Jobs
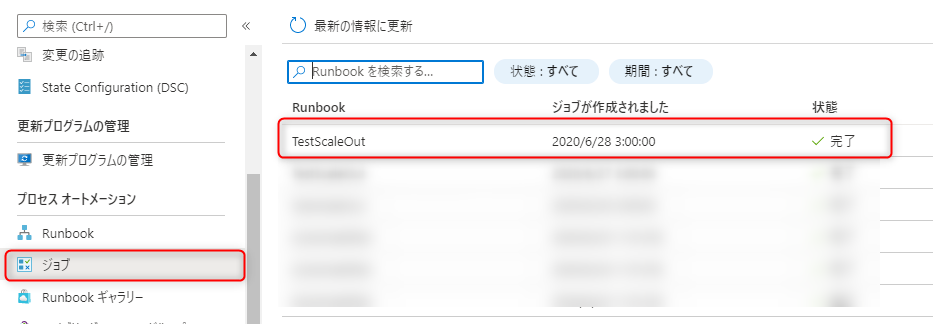
summary
The above steps will enable autoscaling of SQL Database
By the way, to achieve scale-out/in, you just need to create two similar Runbooks and rewrite the plan (-RequestedServiceObjectiveName) part
However, it is only possible to run it at a specified time, and it is a bit of a drawback that it is not possible to run auto-scaling using the essential load status as a threshold...
If anyone knows how to do this, I would be grateful if you could let me know!
Also, although we used DTU this time, I think you can achieve this in a similar way with other purchasing models, so please give it a try
lastly
I am a member of the system development service site "SEKARAKU Lab."
Beyond offers a one-stop service for everything from server design and construction to operation, so if you have any problems with server-side development, please feel free to contact us.
SEKARAKU Lab: [https://sekarakulab.beyondjapan.com/](https://sekarakulab.beyondjapan.com/)
That's all.
Thank you again for this time.

 1
1






