[Must-see for beginners] ChatGPT wrote the Terraform code

table of contents
This is Ken, and I've caught a cold for the first time in about five years, so it's been really tough
It's been a little over a year since I started using AWS services
I thought it would be nice to launch and configure EC2 instances on the console, but it seems like it's becoming increasingly common to implement infrastructure in code. Following this trend, I decided to try launching AWS resources with Terraform. However, anything takes time the first time
So this time, I created the Terraform code together with ChatGPT and then modified it
Environmental information
WSL2
Windows 11
Terraform v1.2.5
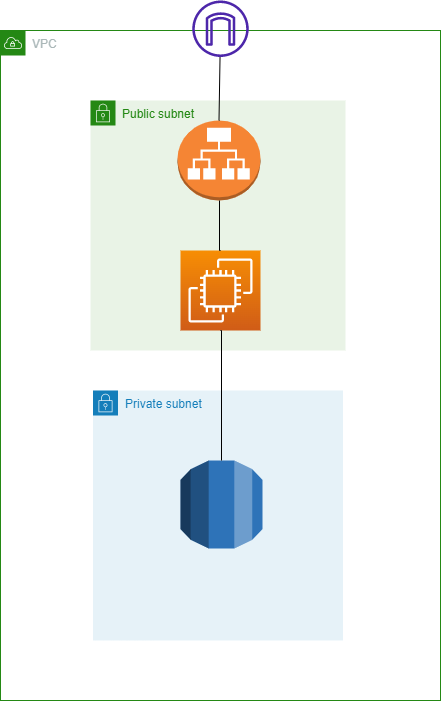
AWS configuration built this time
Prompt words I tried
The prompt input I tried this time was quite simple
I would like to build the following on AWS:
VPC 1
Route table 1
Public subnet 2
Private subnet 2
EC2 1
ALB 1
RDS 1
If you enter a prompt like this, ChatGPT will write out a lot of information for you
As it is, there will not be enough Target Groups or RDS Subnet Groups, so we will ask you to create the missing areas
If you want to continue a basic conversation,
Add a Target Group to the code above
It seems that if you add a keyword like "above," it will inherit the name etc
If they don't take over, I just paste the code and they'll write it in that name whether I like it or not. Also, if I'm unsure, I'll use Google search to check if it's correct
tf file written with the help of ChatGPT
To make this easier to understand, I've combined the files into one and created them without using variables as much as possible. I think it's also possible to create a tf file using variables using ChatGPT, so if you'd like to create one in that format, please give it a try
# Configure provider provider "aws" { region = "ap-northeast-1" } # Create VPC resource "aws_vpc" "main" { cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16" } # Create Internet gateway resource "aws_internet_gateway" "gw" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id } # Create public subnet 1 resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet1" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24" availability_zone = "ap-northeast-1a" map_public_ip_on_launch = true } # Create public subnet 2 resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet2" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id cidr_block = "10.0.2.0/24" availability_zone = "ap-northeast-1c" map_public_ip_on_launch = true } # Create private subnet 1 resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet1" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id cidr_block = "10.0.3.0/24" availability_zone = "ap-northeast-1a" } # Create private subnet 2 resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet2" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id cidr_block = "10.0.4.0/24" availability_zone = "ap-northeast-1c" } # Create route table resource "aws_route_table" "public_route_table" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id route { cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0" gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.gw.id } } # Associate a route table with a public subnet resource "aws_route_table_association" "public_subnet1_association" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet1.id route_table_id = aws_route_table.public_route_table.id } resource "aws_route_table_association" "public_subnet2_association" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet2.id route_table_id = aws_route_table.public_route_table.id } # Create an ALB resource "aws_lb" "alb" { name = "test-alb" subnets = [aws_subnet.public_subnet1.id, aws_subnet.public_subnet2.id] internal = false load_balancer_type = "application" } # Create an EC2 instance resource "aws_instance" "ec2" { ami = "ami-03dceaabddff8067e" instance_type = "t2.micro" subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet1.id key_name = "hogehoge" } # Create a target group resource "aws_lb_target_group" "target_group" { name = "my-target-group" port = 80 protocol = "HTTP" vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id target_type = "instance" } # Associate the ALB with the target group resource "aws_lb_listener" "listener" { load_balancer_arn = aws_lb.alb.arn port = 80 protocol = "HTTP" default_action { type = "forward" target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.target_group.arn } } # Register an instance to the target group resource "aws_lb_target_group_attachment" "target_group_attachment" { target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.target_group.arn target_id = aws_instance.ec2.id port = 80 } # Create RDS resource "aws_db_instance" "rds" { engine = "mysql" instance_class = "db.t2.micro" allocated_storage = 10 engine_version = "5.7" identifier = "my-rds-instance" username = "admin" password = "hogehoge" skip_final_snapshot = true publicly_accessible = false vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.rds_security_group.id] db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.db_subnet_group.name } # Create a security group that allows access to RDS resource "aws_security_group" "rds_security_group" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id ingress { from_port = 3306 to_port = 3306 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } } # Create a DB subnet group resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "db_subnet_group" { name = "my-db-subnet-group" description = "My DB Subnet Group" subnet_ids = [aws_subnet.private_subnet1.id, aws_subnet.private_subnet2.id] }
summary
Although there is a disadvantage for beginners in that they don't know which code is correct, I've recently come to think that it might be a good idea to try out a few and gradually understand which code is easier to write or which is easier to read
Also, the code generated by ChatGPT is not perfect, so in this case, you will probably get an error when you run terraform apply. If that happens, you will definitely need to fix it yourself
However, without thinking it's a hassle, I think that as you investigate what's wrong, you'll gradually come to understand, "Ah, so this is why there's an error! So this way of writing it is wrong."
So, even if you get an error, don't give up, try again and again, and enjoy a rich engineer life

 6
6