Get access logs with AWS ELB!

table of contents

*Chicken Soba Zagin Main Branch (Higobashi, Osaka City)
Hello!
I'm Hide, the Ramen King from Beyond Inc.'s Osaka office.
This is my second post.
This time, I'd like to write about how to obtain access logs using ELB.
Last time, I wrote an article called "Let's use Docker commands easily with Makefile!", so
if you're using Docker, please take a look.
What are the benefits of obtaining access logs with ELB?
Some of you reading this article may be thinking, "Huh? I can keep access logs on the server, so this isn't necessary!"
It is certainly possible to obtain access logs on the server, so
there may not be much benefit to obtaining access logs on ELB...
I, the poster, also thought, "It can be done on the server, so there's no benefit..."
However, what if you want to analyze the access logs?
If your servers are distributed across multiple machines, the access logs will be stored on each server.
Therefore, even if you try to analyze access logs, since they exist on different servers,
integrating and analyzing the access logs takes a lot of time and effort.
For example, you can use CloudWatchLogs to aggregate logs,
but in that case you need to manage permissions with IAM, install an agent on the target server, and
edit the settings in awslogs.conf...
You can also easily collect and utilize logs
using an open-source data log collection tool called fluentd However, this also requires installing and configuring the tool, as well as managing permissions with IAM.
Furthermore, specifying S3 as the aggregation destination can be quite time-consuming.
To analyze access logs, you don't need to configure CloudWatchLogs or fluentd;
you can easily aggregate access logs by enabling the access logs of the ELB in front of the server
All access logs are aggregated in S3, making it easy to store and analyze.
Furthermore, by using AWS Athena or Redshift,
you can easily analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL!
Also, even if a hang occurs and access logs are missing,
you can easily check the ELB access logs to see what happened.
And because ELB is a fully managed service by AWS, you can use it with peace of mind.
Even if a problem occurs, AWS will take responsibility for repairing it.
you can rest assured that you will almost never encounter a situation where you can't get access logs even after enabling ELB.
Now that you understand the benefits of enabling access logs in ELB
, let's take a look at the setup steps!
Setup Procedure
①Go to EC2⇛Load Balancer
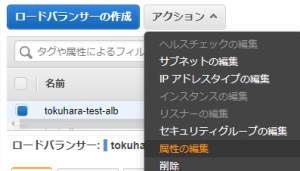
② Click [Edit Attributes] from the Actions menu
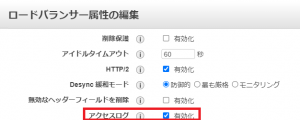
③Select Enable Access Log
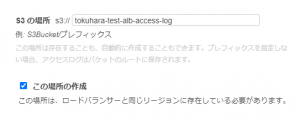
④Specify the bucket name for the S3 location
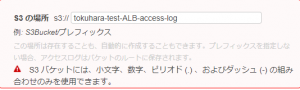
⚠①You can only use a combination of lowercase letters, numbers, periods (.), and dashes (-) in your S3 bucket.
If you enter anything other than the above, you will get an error as shown in the image below.
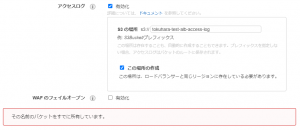
⚠②If the S3 bucket name you entered is already in use, a warning will be displayed and you will be asked to enter a different name
⑤ Check [Create this location] and click Save
⑥Go to S3 and click [Name of the S3 bucket you created]
⑦ Once you have confirmed that the access log file exists in the following directory, the process is complete
*Log files are created every 5 minutes
/Created S3 bucket name/AWSLogs/Elastic Load Balancing account ID number/elasticloadbalancing/Region name/Creation year/Creation month/Creation date/
How to check access logs
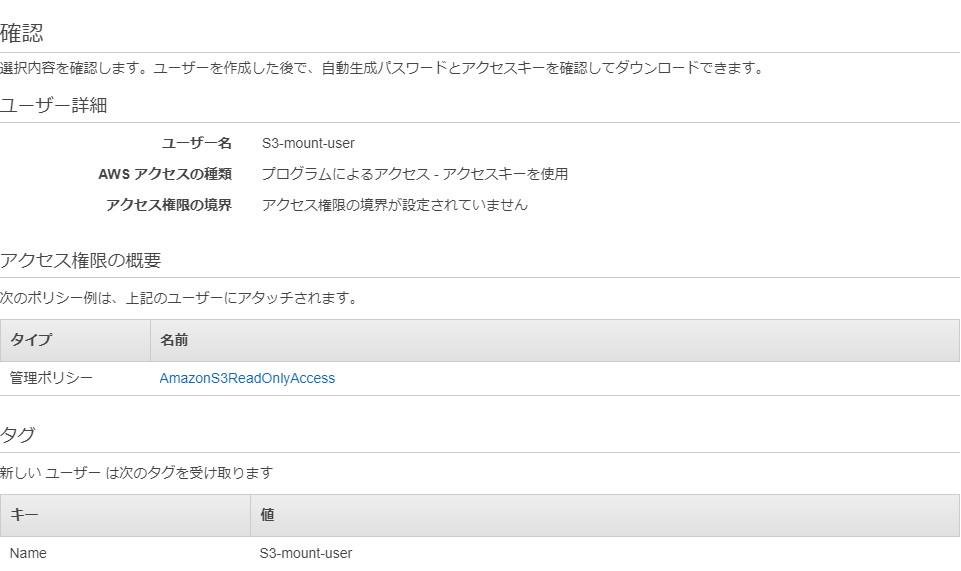
①Go to IAM and click [Create User]
② Fill in the necessary information
*Please make sure to check [Programmatic access] in the access type
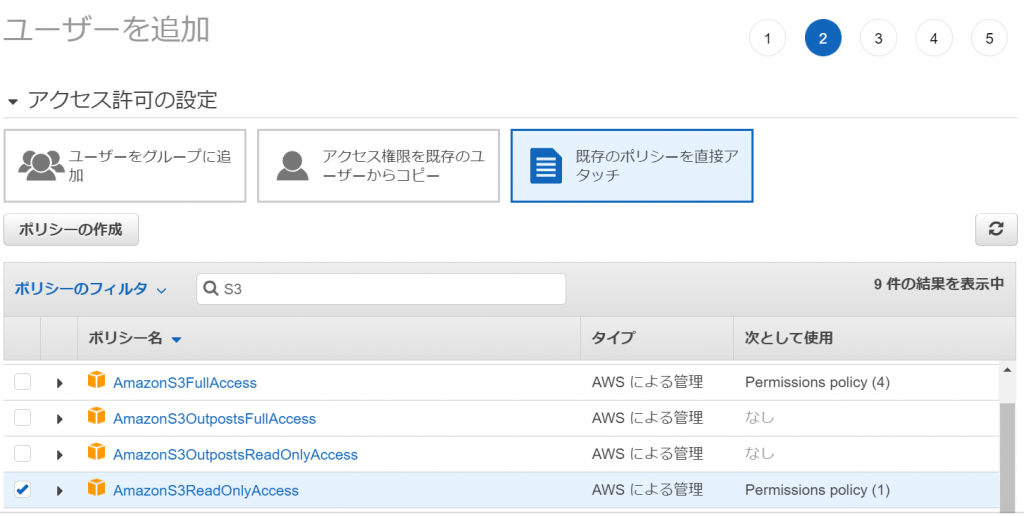
③Select the [AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess] policy
④ Check that there are no input errors and create a user
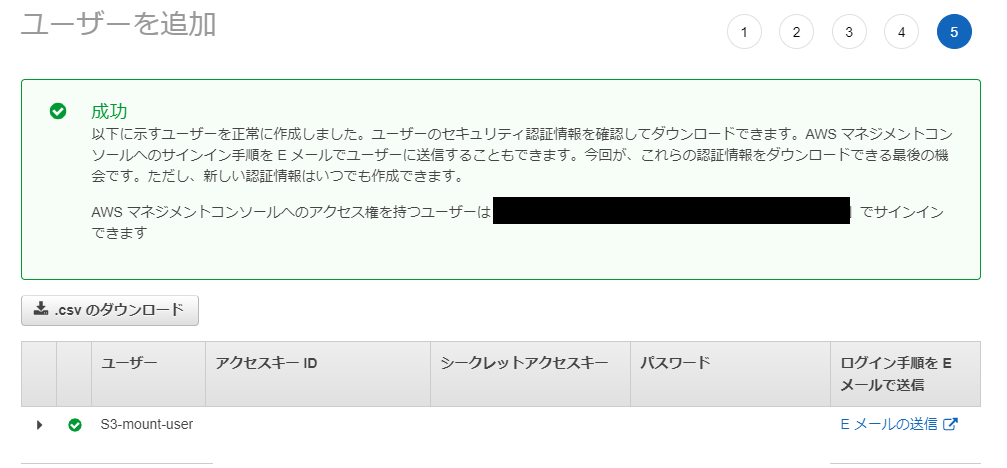
⑤Download the csv file
*Just in case, make a note of your access key and secret access key
⑥Install AWS CLI
*For installing AWS CLI, please refer to the official AWS documentation
⚠Here, we are using Centos 7.
If you are using Amazon Linux 2, it is already installed, so no installation is required.
⑥-① Make sure that Python version is 2.7 or later.
*If Python is not installed, please install it separately.
*On Centos 7, 2.7.5 is installed by default.
python --version Python 2.7.5
⑥-② Install the bundled installer
curl "https://s3.amazonaws.com/aws-cli/awscli-bundle.zip" -o "awscli-bundle.zip" sudo yum install -y unzip unzip awscli-bundle.zip sudo ./awscli-bundle/install -i /usr/local/aws -b /usr/local/bin/aws aws --version
⑦Configuring AWS CLI
aws configure AWS Access Key ID [None]: Enter the access key of the IAM you created AWS Secret Access Key [None]: Enter the secret key of the IAM you created Default region name [None]: Enter the region Default output format [None]: Enter the file format you want to output
⑧ Output access logs
*List files in the S3 bucket using the AWS CLI S3 command aws s3 ls s3://tokuhara-test-alb-access-log/AWSLogs/485076298277/elasticloadbalancing/ap-northeast-1/2021/01/18/ 2021-01-18 08:05:12 884 485076298277_elasticloadbalancing_ap-northeast-1_app.tokuhara-test-alb.20a1e21abd53f9e7_20210118T0805Z_54.65.29.6_53o3j7p0.log.gz *Copy locally aws s3 cp s3://tokuhara-test-alb-access-log/AWSLogs/485076298277/elasticloadbalancing/ap-northeast-1/2021/01/18/485076298277_elasticloadbalancing_ap-northeast-1_app.tokuhara-test-alb.20a1e21abd53f9e7_20210118T2355Z_52.68.106.116_5qgag1lu.log.gz ./ *Check if it has been copied locally ls -l ./ -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 295 Jan 18 23:55 485076298277_elasticloadbalancing_ap-northeast-1_app.tokuhara-test-alb.20a1e21abd53f9e7_20210118T2355Z_52.68.106.116_5qgag1lu.log.gz *Unzip the compressed file gunzip 485076298277_elasticloadbalancing_ap-northeast-1_app.tokuhara-test-alb.20a1e21abd53f9e7_20210118T2355Z_52.68.106.116_5qgag1lu.log.gz *View the access log less 485076298277_elasticloadbalancing_ap-northeast-1_app.tokuhara-test-alb.20a1e21abd53f9e7_20210118T2355Z_52.68.106.116_5qgag1lu.log http 2021-01-21T00:10:51.821814Z app/tokuhara-test-alb/20a1e21abd53f9e7 63.143.XX.XX:45662 - -1 -1 -1 503 - 110 337 "GET http://example.com:80/ HTTP/1.1" "Go-http-client/1.1" - - arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:ap-northeast-1:485076298277:targetgroup/tokuahra-test-tg-ec2/ee1e50320f3398ec "Root=1-6008c68b-4198b51b343e8f127df30e01" "-" "-" 0 2021-01-21T00:10:51.821000Z "forward" "-" "-" "-" "-" "-" "-"
Output and Format
Setting up ELB access logs!! Thank you for your hard work ٩(ˊᗜˋ*)و
However, even if you set up the access logs to be output, you won't be able to investigate the cause if you don't know how to read them...
So, while referring to the official AWS documentation,
the sample access logs obtained from ELB in
the following format, with the values and explanations corresponding to each item clearly displayed.
Please take a look and see what items are included!
http 2021-01-21T00:10:51.821814Z app/tokuhara-test-alb/20a1e21abd53f9e7 63.143.XX.XX:45662 - -1 -1 -1 503 - 110 337 "GET http://example.com:80/ HTTP/1.1" "Go-http-client/1.1" - - arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:ap-northeast-1:485076298277:targetgroup/tokuahra-test-tg-ec2/ee1e50320f3398ec "Root=1-6008c68b-4198b51b343e8f127df30e01" "-" "-" 0 2021-01-21T00:10:51.821000Z "forward" "-" "-" "-" "-" "-" "-"
| field | explanation | Sample Values |
| type | The type of request or connection | http |
| time | The time (UTC) when the load balancer received the request from the client | 2021-01-21T00:10:51.821814Z |
| elb | The name of the ELB | app/tokuhara-test-alb/20a1e21abd53f9e7 |
| client:port | The IP address and port of the client that sent the request | 63.143.XX.XX:45662 |
| target:port | The IP address and port of the target that handled this request | - |
| request_processing_time | The total time elapsed from when the ELB receives the request to when it sends the request to the target | -1 |
| target_processing_time | The total time elapsed from when the ELB sent the request to the target until the target started sending the response headers | -1 |
| response_processing_time | The total time elapsed from when the ELB received the response header from the target to when it started sending the response to the client | -1 |
| elb_status_code | Status code of the response from the load balancer | 503 |
| target_status_code | The status code of the response from the target | - |
| received_bytes | The size of the request received from the client | 110 |
| sent_bytes | The size of the response returned to the client | 337 |
| "request" | The line is enclosed in double quotes in the client request | "GET http://example.com:80/ HTTP/1.1" |
| "user_agent" | A User-Agent string that identifies the client making the request | "Go-http-client/1.1" |
| ssl_cipher | SSL ciphers, set to - if not HTTPS | - |
| ssl_protocol | SSL protocol, set to - if not HTTPS | - |
| target_group_arn | The Amazon Resource Name of the target group | arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:ap-northeast-1:485076298277:targetgroup/tokuahra-test-tg-ec2/ee1e50320f3398ec |
| "trace_id" | The contents of the X-Amzn-Trace-Id header (enclosed in double quotes) | "Root=1-6008c68b-4198b51b343e8f127df30e01" |
| "domain_name" | The SNI domain provided by the client during the TLS handshake (enclosed in double quotes). Set to - if not HTTPS | "-" |
| "chosen_cert_arn" | The ARN of the certificate to be presented to the client (enclosed in double quotes), set to - if not HTTPS | "-" |
| matched_rule_priority | The priority value of the rule that matched the request | 0 |
| request_creation_time | The time when the ELB received the request from the client | 2021-01-21T00:10:51.821000Z |
| "actions_executed" | Actions to be performed when processing the request (enclosed in double quotes) | "forward" |
| "redirect_url" | The redirect target URL in the HTTP response's Location header (enclosed in double quote characters) | "-" |
| "error_reason" | The error reason code (enclosed in double quotes) | "-" |
| "target:port_list" | A space-separated list of target IP addresses and ports (enclosed in double quotes) that handled this request | "-" |
| "target_status_code_list" | A space-separated list of status codes from the target response (enclosed in double quotes) | "-" |
| "classification" | The desync mitigation classification (enclosed in double quotes) | "-" |
| "classification_reason" | The classification reason code (enclosed in double quotes) | "-" |
Fee
Regarding fees, there will be charges for ELB.
According to the official AWS documentation on ELB,
the usage fees for Application Load Balancers in the AWS Tokyo region are as follows:
Next, after the access logs are obtained, they are stored in S3, so S3 charges will be incurred.
According to the official AWS documentation on S3,
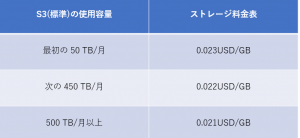
the S3 pricing for the AWS Tokyo region is as follows:
It's a little confusing, but for the first 50 TB, you'll be charged $0.023 per GB per month
For example, if 10GB of log files are accumulated in one month, approximately 24.28 yen will be charged in the first month,
20GB will be accumulated in the second month, so approximately 48.56 yen will be charged, and
30GB will be accumulated in the third month, so approximately 72.54 yen will be charged.
From the month when the capacity exceeds 450TB, a charge of 0.022 USD per GB will be charged.
Looking at the pricing calculations like this, you can see that it is possible to obtain access logs at a very low cost
summary
What do you think?
Were you able to aggregate access logs very easily?
By enabling ELB access logs to aggregate access logs, you can save time and effort, and
there are almost no problems with logs not being able to be acquired, so you can use it stably!
If there is an abnormality in the server and a log error occurs, it can also be easily investigated!
So, be sure to enable ELB access logs
to ensure safe and convenient server operation.
Finally, if you're reading this article and are now interested in S3, then
please check out the article below written by Beyond's Persian Cat!
Thank you for reading the article!

 0
0