[Windows] Automatically delete unnecessary log files periodically

table of contents
Hello.
I'm Kawa from the System Solutions Department. Our uptime has been around 12 minutes recently
Before we knew it, spring was here.
Personally, I love spring the most, as it brings with it a sense of freshness and newness.
I'd like to get rid of any dark secrets from the past, so this time I'll be writing about Windows log rotation. Starting in spring, it's time to start organizing unnecessary files.
Execution environment
Windows 11 Pro
Preparing the batch file
the operation log files of some business application are stored under
C:\Users\testuser\Documents\test This log file is like a perpetual motion machine, with new files added every day. It's a pain to manually delete them one by one. In this article, we'll explain a batch file that will periodically delete these files after two weeks.
First, create a batch file (.bat format) like the one shown below using a text editor
"logrotate.bat"
@echo off setlocal set LOGDIR="C:\Users\testuser\Documents\test" forfiles /P "%LOGDIR%" /M *.log /C "cmd /C Del /S @path" /D -14 exit /B 0
Add this to the Windows Task Scheduler and you're ready to go
Program Description
@echo off setlocal
▶ @echo off disables display of output. Using setlocal ensures that the environment variables used in this program do not affect other programs (localize)
set LOGDIR="C:\Users\testuser\Documents\test"
▶ Assign the path to the target log storage destination to the variable "LOGDIR"
forfiles /P "%LOGDIR%" /M *.log /C "cmd /C Del /S @path" /D -14
▶ It's complicated, so let's break it down into parts
From the help below,
use /P to refer to the relevant path,
/M to search for the file (in this case, a file with the extension ".log"),
/C to execute an arbitrary command, and
/D to check the number of days that have passed. In this case, 14 days = 2 weeks.
forfiles Command Help FORFILES [/P pathname] [/M search mask] [/S] [/C command] [/D [+ | -] {yyyy/MM/dd | dd}] Description: Selects a file (or set of files) and runs a command on that file. This is useful for batch jobs. Parameter List: /P pathname Indicates the path where the search should begin. The default folder is the current working directory (.). /M search mask Search for files by search mask. The default search mask is '*'. /S Tells forfiles to process subdirectories as well (e.g. "DIR /S"). /C command Indicates the command to run for each file. The command string must be enclosed in double quotes. The default command is "cmd /c echo @file". The following variables can be used in the command string: @file - Returns the name of the file. @fname - Returns the file name without the extension. @ext - Returns only the file extension. @path - Returns the full path of a file. @relpath - Returns the relative path of a file. @isdir - Returns "TRUE" if the file type is a directory, or "FALSE" if it is a file. @fsize - Returns the size of a file in bytes. @fdate - Returns the last modified date of a file. @ftime - Returns the last modified time of a file. If you use special characters on the command line, specify the characters in hexadecimal code in 0xHH format (e.g., a tab is 0x09). Internal CMD.EXE commands must be preceded by "cmd /c". /D Date Selects files whose last modified date is on or after (+), or on or before (-), the specified date, using the format "yyyy/MM/dd". Alternatively, selects files whose last modified date is "dd" days after or before the current date. Valid "dd" values are between 0 and 32768. If not specified, "+" is used by default. /? Displays help or usage
"cmd /C Del /S @path"
▶ At this point, use the delete command "Del" and /S @path to delete the specified file from all subdirectories and display the deleted file name
exit /B 0
▶ Adding "/B" to exit will terminate the batch, and specifying the exit code "0" will terminate cmd.exe without returning an error
Execution result
For example, you can debug by manually executing the following from the command prompt.
Place a file somewhere and check the results without the /D option.
testuser> forfiles /P "%LOGDIR%" /M *.log /C "cmd /C Del /S @path" Deleted files - C:\Users\testuser\Documents\test\test.log Deleted files - C:\Users\testuser\Documents\test\test1.log Deleted files - C:\Users\testuser\Documents\test\test2.log
It has been successfully deleted.
If you have made it this far, you are almost there. Let's set up the Task Scheduler.
Adding to Task Scheduler
Open the Task Scheduler using Windows Search or similar.
From the menu, click [Task Scheduler Library] > [Create a task].
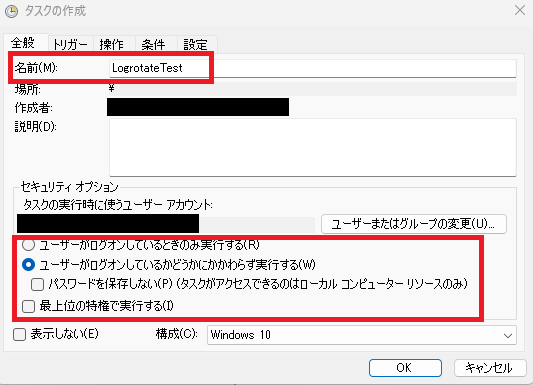
▶ In the [General] tab, you can set the task name and permissions such as "Run only when logged on". Adjust the security options as needed depending on what you want to run
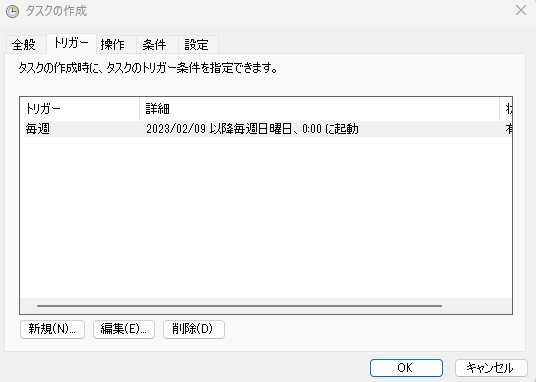
▶ In the [Trigger] tab, you can set the execution timing. In this example, we set it to midnight every Sunday starting from February 9th
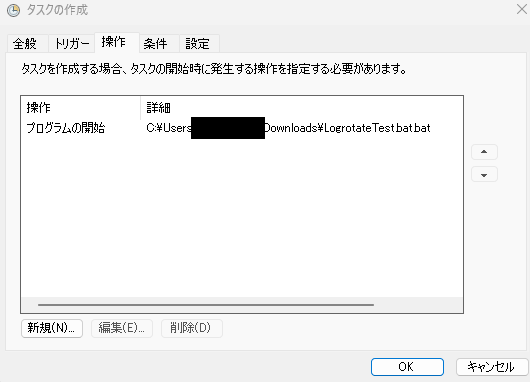
▶ Finally, select the program file you created from the [Operation] tab
If you set it up properly, you won't have to worry about your PC's storage capacity anymore, and you'll definitely be able to do your best from April! Don't look back on the past, just do your best as a new adult!
~Complete~

 29
29






