A handy command to create a dummy file of any size (Windows/Ubuntu)

table of contents
Hello,
from the Brain is Sky Data
System Solutions Department.
The other day, I needed several tens of megabytes of test data when troubleshooting a data transfer.
There are times like this when you need a file of a specific size.
A dummy file can be useful in such situations . This article will show you how to easily create a dummy file using commands in Windows and Ubuntu environments.
Windows
■Execution environment
Windows 11 Pro
In Windows , you can quickly create a file of any size using the
fsutil For example, if you want to create an empty file of 30MB, run the following from the command prompt.
*If the file is not created successfully, run the command prompt with administrator privileges.
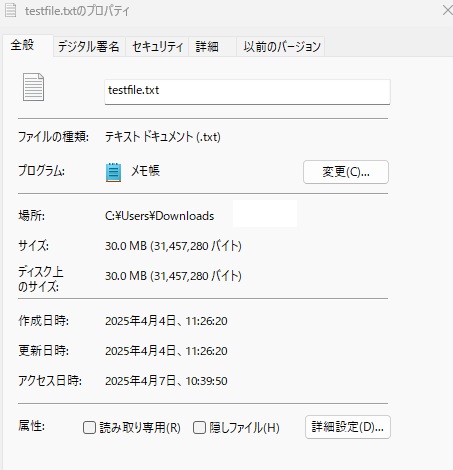
fsutil file createnew testfile.txt 31457280
This command specifies the file size in
bytes 30MB = 30 * 1024 * 1024 = 31,457,280 bytes.
A file of exactly 30MB was created
Is the inside empty?
When you read a file created with the fsutil command, the file contents are returned as all zeros (0x00). This means that the file does not contain any "non-zero" data.
To be precise, the read data is repeated "0x00" in hexadecimal, so it looks like a file filled with only zeros.
It's important to note that this zero data isn't actually read from a block on disk -
space is reserved on the disk, but the data is not physically written to that unused space, so the zero data is returned immediately without actually accessing the disk.
Ubuntu
In Linux, fallocate command works similarly.
For example, to create a 30MB file in Ubuntu, run the following:
■Execution environment
Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS
$ fallocate -l 30M dummyfile.dat
▼If you check the contents, it will return the byte sequence “0x00” just like before
$ less dummyfile.dat "dummyfile.dat" may be a binary file. See it anyway? ^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@ ^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^ @^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@ ^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^ @^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^@^....
You can specify the size directly in MB or GB with the -l option, which is easier than Windows
That's how to create an empty file of a specified size for each OS!
complete

 6
6






