[Training Review] This is what happens when you use Google Cloud with the same feeling as AWS

table of contents
Introduction
Nice to meet you. I'm Paru, a first-year infrastructure engineer in the System Solutions Department, graduating in 2024.
I'm a liberal arts graduate, but I'm working hard every day to become a fully-fledged engineer!
This time, as a review of the training,
I will introduce the confusion that a person with no IT experience faced when building a server using Google Cloud in a role-playing exercise after learning about AWS in a classroom training session.
For more details on the training content, please see the previous article below.
[Biyoben #41] We held a study session on the contents of training for new graduate engineers!
Please also take a look at our previous articles on AWS, which are extremely easy to understand for beginners
[AWS Beginners] A quick explanation of what Amazon VPC is!
Premise: A rough summary of terms
Even if the services are similar, AWS and Google Cloud use different names
.
| AWS | Google Cloud | meaning |
| VPC | VPC network | Virtual Network |
| Availability Zones | zone | Geographically distant data centers |
| Security Groups & Network ACLs | Firewall Rules | Communication control function |
| Elastic Load Balancing | Cloud Load Balancing | Ability to distribute received traffic across multiple targets |
Network Configuration
Now, let's look at the differences in network configuration, which was the first thing we ran into.
The network configurations of AWS and Google Cloud are significantly different.
Please see below.
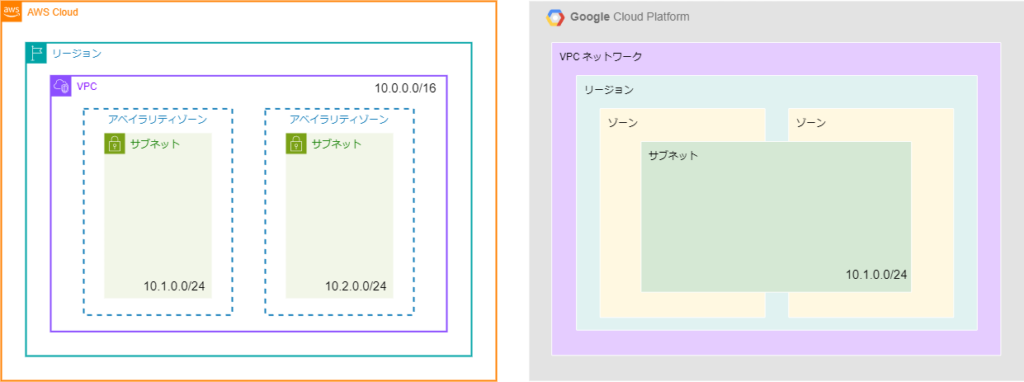
AWS network configuration
In AWS, VPCs exist within regions .
You must
also add an IP address range to the VPC and the subnet The subnet's IP address range is allocated from the VPC's IP address range.
Google Cloud Network Configuration
In Google Cloud, exist
within the VPC network In Google Cloud, the VPC itself is a global entity, and the difference comes from the configuration in which a region is specified within it.
Also, IP address ranges only added to subnets .
In the case of Google Cloud, you can expand or change the network design simply by creating a new subnet.
Bonus: Database placement
Incidentally, the network configurations and database placement methods are different.
AWS builds RDS within a VPC created by the user .
CloudSQL in a VPC dedicated to CloudSQL , not within the user's VPC VPC Peering is required
to connect the user's VPC with CloudSQL. If you build it the same way as AWS, you may be confused and find that the database and VPC cannot be associated.
Differences in communication control methods
You might want to block access from aggressive IP addresses, or you might want to allow access only from specific IP addresses in a development environment.
Communication control methods vary depending on the server.
Here, we'll compare the differences in communication control methods between AWS and Google Cloud.
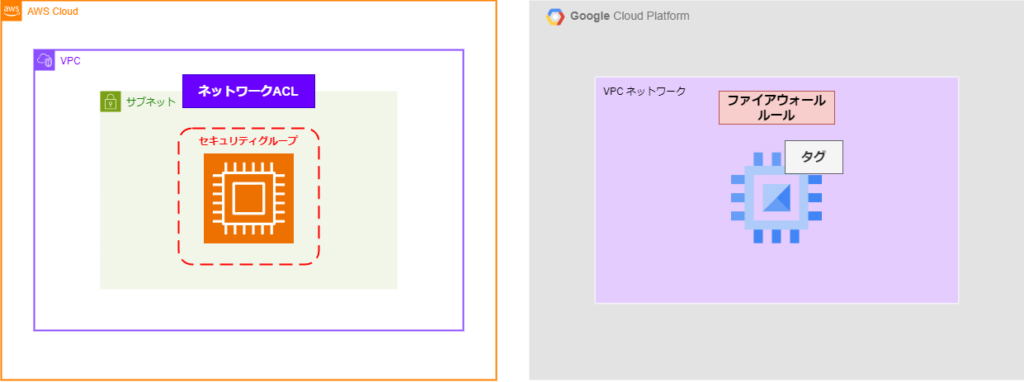
AWS Security Groups and Network ACLs
In AWS, you can control communication on an instance-by-instance basis using security groups and on a subnet-by-subnet basis using network ACLs
Security groups allow you to set rules that
allow access to individual resources such as EC2 instances They can be used to manage inbound and outbound traffic between AWS resources, or between resources and clients, and strengthen security. Network ACLs allow you to set rules that
deny access to subnets . Since
you can deny access to specific IPs and ports, you can flexibly set network security policies.
Google Cloud Firewall Rules
Communication control for Google Cloud can be configured using
firewall rules There are no changes to the services handled by resources or networks, as there are with AWS.
Firewall rules can be used to create inbound (receiving) and outbound (sending) settings, as well as allow/deny settings.
Also, if you want to apply rules to resources, you can assign them using
tags If you want to apply a firewall to resources such as instances, you can apply the rule by setting tags when creating the firewall rule and then assigning the tag to the target resource.
When I was just learning to use tags during my training, I remember having a hard time creating a large number of rules because I didn't really understand how to use tags.
Load Balancer Types
A load balancer is a service that can distribute the load on multiple servers by linking them to them.
AWS has four types , while Google Cloud has
10. Incidentally, the service names are also unique, with AWS having Elastic Load Balancing and Google Cloud having
Cloud Load Balancing Here, we will compare the load balancers of AWS and Google Cloud and look at why there are so many different types.
The table below shows the types of load balancers available for each.
| AWS | Google Cloud |
| Application Load Balancer (ALB) Network Load Balancer (NLB) Gateway Load Balancer (GLB) Classic Load Balancer (CLB) |
Application External Global Load BalancerApplication External Regional Load BalancerApplication Internal Global Load BalancerApplication Internal Regional Load BalancerNetwork External Global Proxy Load BalancerNetwork External Regional Proxy Load BalancerNetwork Internal Global Proxy Load BalancerNetwork Internal Regional Proxy Load BalancerNetwork External Regional Pass-Through Load BalancerNetwork Internal Regional Pass-Through Load Balancer |
Elastic Load Balancing (AWS load balancer)
There are several types of AWS load balancers:
Application Load Balancer (ALB) - Supports HTTP and HTTPS traffic.
Network Load Balancer (NLB) - Distributes large volumes of traffic with low latency.
Gateway Load Balancer (GLB) - Can extend third-party virtual networks.
Classic Load Balancer (CLB) - Like ALB and NLB, it distributes load across multiple instances, but is the only one that supports the EC2-Classic network.
You can choose an AWS load balancer from the above options based on your needs
Cloud Load Balancing (Google Cloud load balancer)
Next, we'll briefly explain Google Cloud's load balancers.
Unlike AWS, where you can choose from four different load balancers, you can select the one that best suits your needs. You
can set up a load balancer by following the steps below.
Application type or network typeApplication
type: Load balancing at the application layer (receives requests at layer 7 of the OSI reference model)
Network type: Load balancing at the network layer (receives requests at layer 3 or 4 of the OSI reference model)
External or internal
External: Receives traffic from the Internet
Internal: Receives traffic only within the VPC
Global or
Regional? Global: Deployed globally, with settings reflected to server resources deployed at edge PoPs (points for connecting to the Google Cloud network from the Internet).
Regional: Deployed within a specific region, with settings reflected only within that region.
Proxy or pass-through type (network type only)
Proxy type: Receives communication requests from clients and can perform processes such as header rewriting and redirection
. Pass-through type: Passes communication from clients directly.
By following this step-by-step setup, you can set up load balancers such as an "application external global load balancer" or an "internal network regional pass-through load balancer," giving you a total of 10 different types to choose from
The large number of types makes it difficult to get started, and I couldn't understand them during training, and I was annoyed
by the sheer number of options. However, looking at it again, I think that the ability to select a load balancer based on detailed conditions is an advantage of the Google Cloud load balancer.
summary
This memorable first blog post was about the confusion I experienced as an IT novices when building a server using Google Cloud after learning a little about AWS. It
was also a good opportunity for me to review my training and learn more about AWS and Google Cloud.
I hope this blog will be helpful for IT novices who are new to the cloud!
Reference websites:
Comparing AWS, Azure, and GCP - IaaS edition
Comparing AWS/Azure/GCP services - Network edition
Understand from scratch! The big picture of GCP network security
Configuring replication from MySQL on AWS EC2 to GCP Cloud SQL
Understanding the world of Google Cloud load balancers from the AWS perspective
[AWS Introduction] What is AWS ELB? Introducing the types, features, and pricing of load balancers
Understanding the Google Compute Engine firewall #gcpja
How to use AWS ACLs and security groups

 9
9






